EFFECT OF CORROSION ON TEARING PERFORMANCE OF STEEL LINER OF NUCLEAR CONTAINMENT STRUCTURES
-
摘要: 为研究锈蚀对核安全壳结构钢衬里撕裂的影响,该文对36个不同锈蚀率的钢衬里板进行了单轴拉伸试验,分析了锈蚀钢衬里板的力学性能退化机理和退化规律;建立了锈蚀钢衬里板的本构模型;根据试验结果,提出了考虑不同锈蚀率的钢衬里撕裂准则和锈蚀模拟方法;通过数值模拟,分析了锈蚀对安全壳钢衬里撕裂的影响;最后对比了该文模拟方法与美国核管理委员会(NRC)方法的差异,并给出了NRC方法中锈蚀影响系数的取值建议。结果表明:随锈蚀率增大,钢衬里板的弹性模量变化不大,但其屈服强度、峰值强度、峰值应变和断裂应变大致呈线性退化规律;该文建立的锈蚀钢衬里板的本构模型与试验结果吻合良好;随锈蚀率增大,安全壳钢衬里发生撕裂时的内压逐渐降低,且当锈蚀率为50%时,内压降低29.06%;与NRC方法相比,该文方法能直观反映不同锈蚀率对钢衬里的影响,更能接近实际锈蚀情况;对于NRC所建议的锈蚀影响系数,锈蚀率小于20%时,可取上限值,锈蚀率为20%~40%时,建议取最佳估值,而锈蚀率超过40%后,应当取下限值。该文研究工作可为安全壳钢衬里锈蚀后的性能评估提供借鉴和参考。Abstract: To study the effect of corrosion on the tearing performance of the steel liner of nuclear containment structures, 36 steel liner plates with different corrosion rates are tested under uniaxial tension. The degradation mechanism and the law of mechanical properties of corroded steel liners are analyzed. The constitutive model of corroded steel liners is established. Based on the test results, a tearing criterion and a numerical simulation method for corroded steel liner are proposed. The effect of corrosion on the tearing of the steel liner of containment is analyzed by numerical simulation. Finally, the difference between the simulation method and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) method is compared, and a suggestion on the value of the corrosion influence coefficient in the NRC method is developed. The results show that: the elastic modulus of the steel liner is not affected by corrosion, but with the increase of corrosion rate, the yield strength, peak strength, peak strain and, fracture strain show linear degradation. The constitutive model of the corroded steel liner established agrees well with the experimental results; with the increase in corrosion rate, the internal pressure at the time of steel liner tearing gradually decreases, and when the corrosion rate is 50%, the internal pressure decreases by 29.06%. Compared with the NRC simulation method, the method proposed can directly reflect the influence of corrosion on the steel liner and is closer to the actual corrosion situation. For the corrosion influence coefficient recommended by NRC, the upper bound can be selected when the corrosion rate is less than 20%. The best estimation is recommended when the corrosion rate is 20% ~ 40%, and the lower bound should be selected when the corrosion rate exceeds 40%. The research work can provide a reference for the performance evaluation of containment with a corroded steel liner.
-
随着我国核电事业的蓬勃发展,核电技术已实现从“跟跑”到“领跑”的飞跃,而核安全问题一直是人们关注的重点。安全壳结构是核安全纵深防御设计体系中至关重要的一道防止放射性物质泄漏屏障[1-2],钢衬里在保证其密封性方面起主要作用[3]。自1991年我国第一台核电机组并网发电起,至今已近30年,部分现役机组的安全壳结构存在不同程度的老化问题,而钢衬里锈蚀是安全壳结构老化的主要形式之一[4-5]。美国Sandia实验室进行的系列安全壳试验表明,钢衬里撕裂时混凝土早已开裂[6-8],从而钢衬里的撕裂性能直接决定了安全壳在超设计基准事故下的密封性[9]。因此,研究锈蚀对安全壳钢衬里撕裂的影响具有重要意义。
由于安全壳结构的特殊性,锈蚀对钢衬里撕裂的影响一般是先通过试验,研究锈蚀钢衬里板的力学性能,然后,根据试验结果开展安全壳钢衬里锈蚀后的数值模拟来进行综合分析。目前,关于钢衬里锈蚀的研究资料以国外为主,国内鲜有报道。CHERRY[10]对美国核电厂安全壳所用钢衬里板进行了锈蚀试验研究,结果表明:锈蚀会显著削弱钢衬里板的极限强度和极限拉伸应变。美国核管理委员会(NRC)在CHERRY[10]的研究基础上,提出了钢衬里锈蚀模拟方法和有限元分析中考虑锈蚀的钢衬里撕裂准则[11-12]。SPENCER等[12]、SMITH等[13]和PETTI等 [14-15]按照NRC给出的方法对不同类型的安全壳在钢衬里锈蚀情况下的密封性进行了评估,研究表明:锈蚀会导致钢衬里提前发生撕裂,增大安全壳在事故荷载下发生核辐射泄漏的风险。ALHANAEE等[16]同样按照NRC给出的方法对APR1400预应力混凝土安全壳进行了钢衬里锈蚀影响分析,研究表明:钢衬里锈蚀对安全壳结构的极限承载力基本没有影响,但锈蚀会引起钢衬里局部产生应变集中,容易引起安全壳发生功能性失效。
目前关于锈蚀钢衬里力学性能的研究非常少,CHERRY[10]试验考虑的最大锈蚀率仅20%,试验数据不够充分,未能得到不同锈蚀程度对钢衬里力学性能的影响规律,并且试验试件的厚度与实际安全壳钢衬里的厚度差别也很大。NRC提出的锈蚀模拟方法是以折减钢衬里厚度的方式来考虑锈蚀区域钢衬里承载能力的削弱,但忽略了锈蚀钢板本身材料性能的退化。同时,NRC提出的锈蚀钢衬里撕裂准则是以引入锈蚀影响系数来考虑锈蚀对钢衬里板延性的影响,不同程度的锈蚀对钢衬里的影响是不同的,然而,该系数仅是根据CHERRY[10]和BRUNEAU等[17]的试验结果给出了三个建议值,并不能直观反映锈蚀率和锈蚀影响系数之间的关系,且不同锈蚀率下建议值如何选取也不明确。
针对以上问题,本文研究了钢衬里板锈蚀后的力学性能,分析了不同锈蚀率下其力学性能的退化机理和退化规律;建立了不同锈蚀率下钢衬里板的本构模型;基于试验结果,提出了考虑不同锈蚀率的钢衬里撕裂准则和锈蚀模拟方法;利用Submodel分析方法,探究了锈蚀对安全壳钢衬里撕裂的影响;最后对比了本文模拟方法与NRC方法的差异,并给出了NRC方法中锈蚀影响系数的取值建议。本文研究工作可为安全壳钢衬里锈蚀后的性能评估提供借鉴和参考。
1 锈蚀钢衬里拉伸性能试验研究
1.1 试件制备与锈蚀
本文试验所用钢衬里材料为国内某核电厂安全壳所用6 mm厚P265GH型钢板,其力学性能符合《欧洲压力容器用钢板标准》(BS EN 10028-2: 2017)[18]要求。拉伸试件的设计参照《金属材料拉伸试验第1部分:室温试验方法》(GB/T228.1−2010)[19],其尺寸和形状如图1所示。试验考虑了6组锈蚀率(0%~50%),每组锈蚀率下各6个试件,各组试件命名方式为“L-锈蚀率-编号”。相关调研报告指出,安全壳钢衬里一般产生内侧或外侧的单面锈蚀[4, 20]。为更接近实际情况,本文试件采用电化学加速锈蚀方法对试件进行单侧锈蚀[21],试件未锈蚀一侧采用防锈漆和环氧树脂进行保护。各组试件锈蚀完成后,首先按照规范[22]的要求,对该组所有锈蚀试件进行酸洗,清除钢板上的锈蚀层,然后再进行锈蚀率的测量和拉伸试验。
实际安全壳钢衬里锈蚀程度评估时,通常以锈蚀深度和面积作为指标,因此本文以锈蚀试件的截面损失率作为锈蚀率,其计算公式如下:
η=(1−d1w1d0w0)×100% (1) 式中:
η 截面损失率;d0 和w0 分别为未锈蚀试件的初始平均厚度和宽度;d1 和w1 分别为锈蚀后的试件去除环氧保护层并酸洗清除锈蚀层后的平均厚度和宽度。1.2 加载和测量方案
试件采用AG-X电子万能试验机进行单轴拉伸,拉伸各阶段的加载速率按标准[19]执行。试验前在试件中部标记50 mm长的标距段,标距段的变形由引伸计实时监测,试验装置如图2所示。
1.3 试验结果与分析
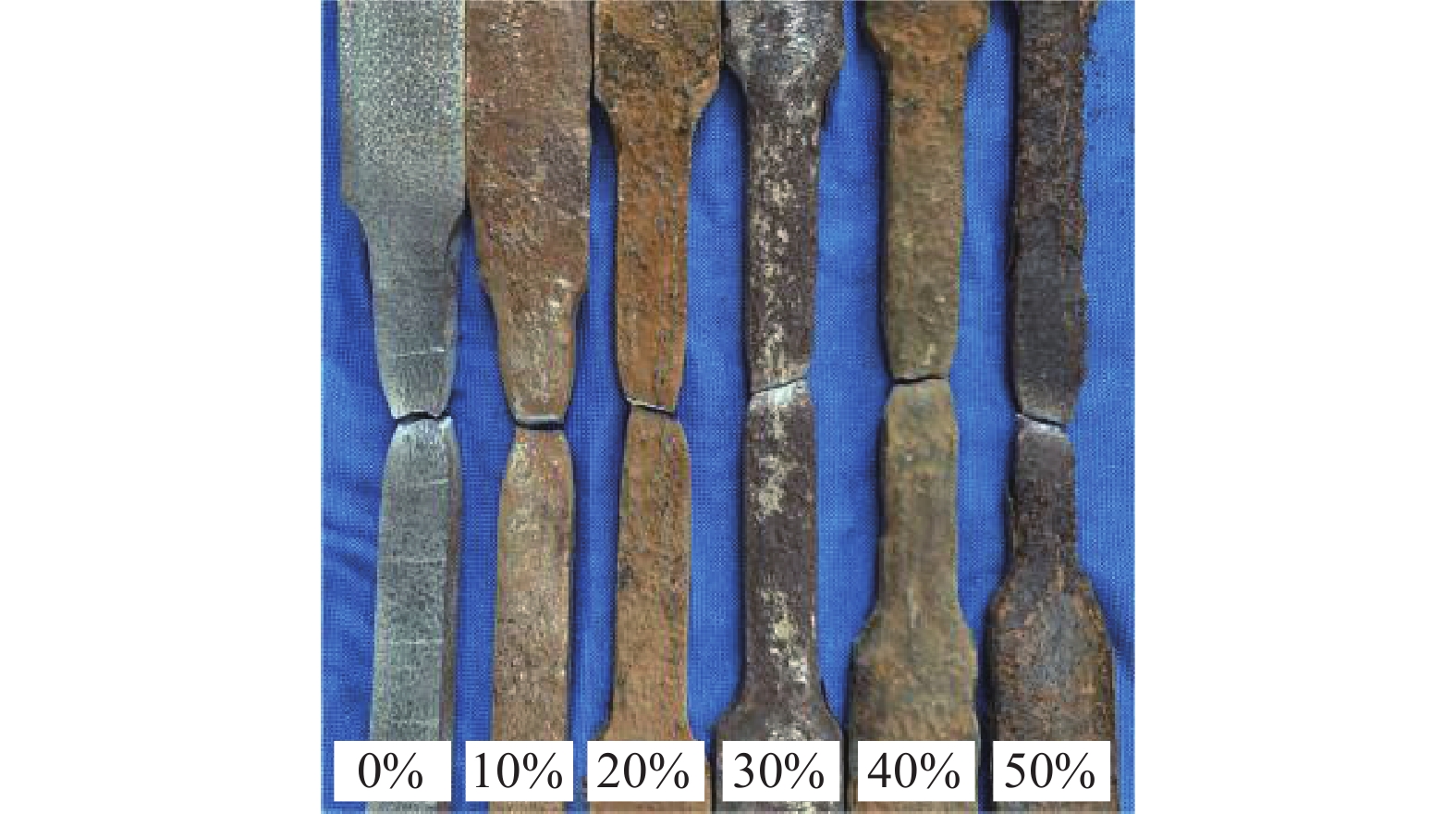
不同锈蚀率下钢衬里板的拉伸破坏形式如图3所示,可以看出,锈蚀率越大,钢板截面损失越严重,因不均匀锈蚀产生的锈坑也越多。表1为各组试件的试验结果,图4为各组代表性试件的拉伸应力-应变曲线。
表 1 钢衬里板拉伸试验结果Table 1. Tensile test results of steel liner plate试件组 弹性模量Es
平均值/MPa屈服强度fy
平均值/MPa峰值强度fp
平均值/MPa峰值应变ɛp
平均值断裂应变ɛu
平均值L-0% 203 958 310.57 431.14 0.2657 0.4363 L-10% 201 631 290.42 394.12 0.2105 0.3009 L-20% 202 142 264.10 379.22 0.1792 0.2414 L-30% 200 109 267.21 364.65 0.1425 0.1935 L-40% 201 966 248.34 361.25 0.1413 0.1899 L-50% 199 694 231.02 335.07 0.1095 0.1464 注:以上各强度值为试件锈蚀后的荷载除以锈蚀后的截面面积;部分试件断裂不在测量标距内,相应的数据已舍去。 由表1和图4可以看出:随锈蚀程度的增大,钢衬里板的弹性模量
Es 变化比较小,而其屈服强度fy 、峰值强度fp 、峰值应变εp (峰值强度所对应的应变)和断裂应变εu 则逐渐降低;锈蚀率为50%时,钢衬里板的断裂应变平均值降低66.45%,表明锈蚀会造成钢板的延性显著退化;锈蚀率较低时,钢板具有明显的屈服点和屈服平台,而当锈蚀率达到30%后,其屈服点不再明显,且屈服平台逐渐变短甚至消失。为直观反映锈蚀对钢衬里板各力学性能参数的影响规律,本文以锈蚀率
η 为自变量,对各锈蚀率下钢板的Es 、fy 、fp 、εp 和εu 进行统计分析,如图5和图6所示。由图5可以看出,不同锈蚀率下钢板的弹性模量近似沿一水平直线分布,因此可近似认为锈蚀对钢板弹性模量的影响不明显[23-24]。由图6可以看出,锈蚀钢板其余各力学性能参数随锈蚀率的增加,大致满足如下线性退化规律:
M=1−kη,0⩽ (2) 式中:
M 为钢板各力学性能参数的相对值,即M({f_{\text{y}}}){\text{ = }}{f_{\text{y}}}/{f_{{\text{y0}}}} ,M({f}_{\text{p}})\text{=}{f}_{\text{p}}/{f}_{\text{p0}} ,M({\varepsilon _{\text{p}}}){\text{ = }}{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}}/{\varepsilon _{{\text{p0}}}} ,M({\varepsilon _{\text{u}}}){\text{ = }}{\varepsilon _{\text{u}}}/{\varepsilon _{{\text{u0}}}} ;其中{f_{{\text{y0}}}} 、{f_{{\text{p0}}}} 、{\varepsilon _{{\text{p0}}}} 和{\varepsilon _{{\text{u0}}}} 分别表示未锈蚀试件的屈服强度、峰值强度、峰值应变和断裂应变平均值;k为各参数的退化系数,对于{f_{\text{y}}} 、{f_{\text{p}}} 、{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} 和{\varepsilon _{\text{u}}} 分别取0.46、0.37、1.1和1.28。锈蚀造成钢衬里板力学性能退化的原因为:锈蚀通常是非均匀的,容易使钢板发生点蚀而形成锈坑,进而在钢板上形成多个应力集中区域,导致其强度降低[23];点蚀形成的锈坑会增大钢板内部应力三轴度,减小其等效塑性断裂应变,且局部点蚀损伤会加速钢板内部裂纹萌生和扩展,使其容易在较低的应变水平下发生断裂,从而导致钢板的延性显著退化[25];此外,锈坑较深位置处的应力和应变增长速度比未锈蚀区域快,造成钢板的屈服平台变短。锈蚀率越大,钢板非均匀锈蚀程度越大(如图3所示),对其力学性能的影响也越加严重。
2 锈蚀钢衬里本构计算模型
由图4可以看出,钢衬里板拉伸应力-应变曲线可划分为弹性段、屈服段、强化段和颈缩段四个部分。通过对试验曲线上的特征点和试验数据进行统计分析,本文提出钢衬里板在不同锈蚀率下的本构模型表达式为:
{\sigma _{\text{s}}} = \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{E_{\text{s}}}{\varepsilon _{\text{s}}}{\text{ }}\;,\qquad0 \leqslant {\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} < {\varepsilon _{\text{y}}}{\text{ }} \\& {f_{\text{y}}}\;,{\text{ }}\quad\qquad{\varepsilon _{\text{y}}} < {\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} \leqslant {\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}} \\& {f_{\text{y}}}\left[ {1 + \frac{{{\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}}}\Bigg(\frac{{{f_{\text{p}}}}}{{{f_{\text{y}}}}} - 1\Bigg)\exp \Bigg(1 - \frac{{{\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}}}\Bigg)} \right]{\text{ }} ,\\ &\qquad\qquad{\text{ }}{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}} < {\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} \leqslant {\varepsilon _{\text{u}}}{\text{ }} \end{aligned} \right. (3) 式中:
{\sigma _{\text{s}}} 为钢衬里板应力;{\varepsilon _{\text{s}}} 为钢衬里板应变;{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}} 为钢衬里板强化点应变。本构模型中,近似认为不同锈蚀率下钢衬里板的弹性模量保持不变,进而其屈服应变可由屈服强度计算得到。不同锈蚀率下的
{f_{\text{y}}} 、{f_{\text{p}}} 、{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} 和{\varepsilon _{\text{u}}} 可由式(2)计算。对于强化点应变{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}} ,受不均匀锈蚀的影响,该参数具有很大的离散性。为形成统一的本构表达式,本文根据试验数据对{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}} 进行线性拟合,关系式如下:M({\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}) = \frac{{{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh0}}}}}} = 1 - {\text{1}}{\text{.48}}\eta (4) 式中:
M({\varepsilon _{{\text{sh}}}}) 为锈蚀钢板强化点应变相对值;{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh0}}}} 为未锈蚀钢板强化点应变平均值,本文试验{\varepsilon _{{\text{sh0}}}} = 0.020\;79 ;式(4)相关系数{R^2}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.5695}} 。根据本构模型,计算得到不同锈蚀率下钢衬里板的拉伸应力-应变曲线,将其与试验实测曲线进行对比,如图7所示,可以看出两者吻合良好。
3 安全壳钢衬里锈蚀数值模拟
3.1 安全壳全局模型
本文以某现役核电厂预应力混凝土安全壳结构为例,研究锈蚀对钢衬里撕裂的影响,其结构简图如图8所示。
该安全壳结构由穹顶、环梁、筒体、钢衬里和底板组成,底板表面至穹顶总高61.7 m,穹顶壁厚0.8 m。安全壳筒体内径18.5 m,壁厚0.9 m,其外侧对称设置了4个扶壁柱。钢衬里通过栓钉和角钢锚固在安全壳内壁,厚度6 mm。安全壳结构内布置普通钢筋和预应力筋系统,预应力筋包括竖向钢束、环向钢束和Gamma钢束,通过底板、扶壁柱和环梁进行锚固。此外,安全壳筒体内设置了设备闸门和应急闸门等多个贯穿件洞口。
3.1.1 材料本构关系
安全壳混凝土强度等级为C50,弹性模量取34.5 GPa。混凝土采用塑性损伤模型进行模拟[26],其单轴受压和受拉本构关系分别采用文献[27]和文献[28]建议的模型,即:
{\sigma _{\text{c}}} = \dfrac{{{E_{\text{c}}}{\varepsilon _{\text{c}}}}}{{1 + (R + {R_E} - 2)\left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{\text{c}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}} \right) - (2R - 1){{\left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{\text{c}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}} \right)}^2} + R{{\left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{\text{c}}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}} \right)}^3}}} (5) {\sigma _{\text{t}}} = \left\{ \begin{aligned} & {E_{\text{c}}}{\varepsilon _{\text{t}}}\;,\quad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad{\varepsilon _{\text{t}}} {\leqslant} {\varepsilon _{{\text{cr}}}} \\& {f_{\text{t}}}{{\cdot}}\exp \left[ { - 2({\varepsilon _{\text{t}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\text{cr}}}})/{\varepsilon _{{\text{tu}}}}} \right]{\text{ }}\;,\qquad{\varepsilon _{\text{t}}} > {\varepsilon _{{\text{cr}}}} \end{aligned} \right. (6) 式中:
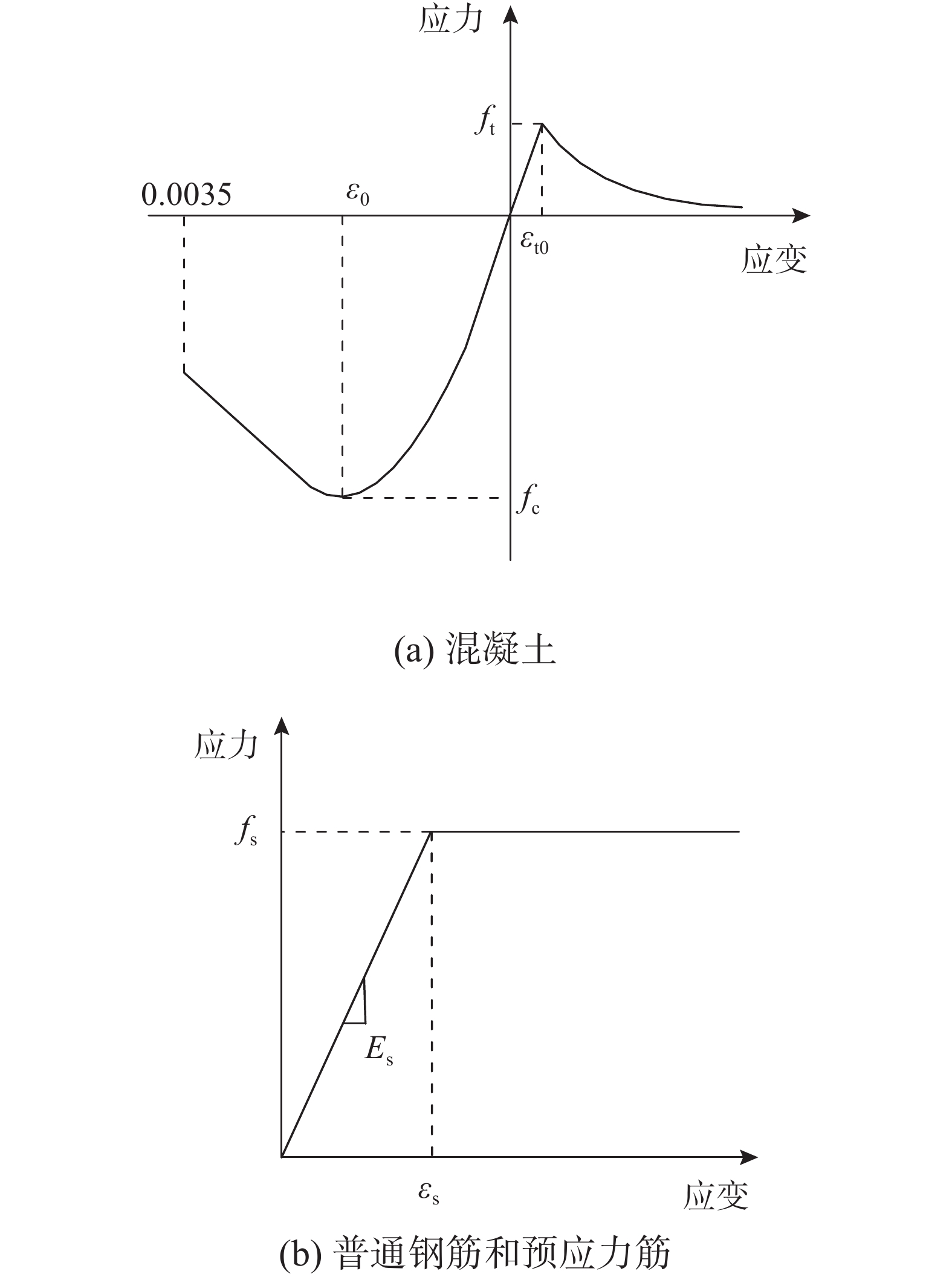
R = \dfrac{{{R_E}\left( {{R_\sigma } - 1} \right)}}{{{{\left( {{R_\varepsilon } - 1} \right)}^2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_\varepsilon }}} ,{R_E} = \dfrac{{{E_{\text{c}}}}}{{{E_0}}} ,参考文献[29],可取{R_\sigma } = 4 ,{R_\varepsilon } = 4 ;{\sigma _{\text{c}}} 和{\varepsilon _{\text{c}}} 分别为混凝土压应力和压应变;{E_{\text{c}}} 和{E_0} 分别为混凝土的初始弹性模量和割线模量;{\varepsilon _0} 为混凝土峰值压应力对应的应变;{\sigma _{\text{t}}} 和{\varepsilon _{\text{t}}} 分别为混凝土拉应力和拉应变;{f_{\text{t}}} 为混凝土抗拉强度;{\varepsilon _{{\text{cr}}}} 为混凝土开裂应变;{\varepsilon _{{\text{tu}}}} 为混凝土极限拉应变。安全壳普通钢筋和预应力筋的本构关系采用文献[30]中建议的理想弹塑性模型,两者的弹性模量分别取200 GPa和195 GPa,泊松比皆取0.3。由于本文重点关注钢衬里,为更加接近真实情况,钢衬里本构关系采用式(3)提出的本构模型。混凝土和钢筋的本构关系如图9所示。
3.1.2 网格划分与分析步
安全壳混凝土以C3D8R实体单元为主,局部采用C3D6R单元。钢衬里以S4壳单元为主,贯穿件洞口处采用少量S3单元, 并通过蒙皮法与混凝土单元共节点[31]。预应力筋采用T3D2桁架单元,普通钢筋采用SFM3D4和SFM3D3面单元进行等效。预应力筋和普通钢筋按照安全壳实际配筋布置情况嵌入到混凝土中,不考虑相互之间的滑移[32]。为兼顾计算精度和效率,安全壳整体网格尺寸取0.8 m,贯穿件洞口等刚度不连续区域进行网格加密。安全壳全局模型网格划分如图10所示。
本文安全壳全局模型非线性分析包含两个分析步:在第一个分析步中同时施加预应力和重力荷载,预应力采用降温法模拟;在第二个分析步中沿结构内表面施加线性增长的内压荷载。
3.2 锈蚀钢衬里子模型
3.2.1 子模型建立与锈蚀区划分
NRC调研报告显示,安全壳钢衬里锈蚀区域一般比较小[4, 20]。为有效捕捉锈蚀区域的应变集中,有限元模型和网格必须足够精细。然而,安全壳结构尺寸较大且较复杂,难以建立精细化的全局模型对锈蚀区进行分析。为此,本文首先对全局模型进行计算得到计算结果,然后根据全局模型建立所要研究区域的精细化子模型;通过ABAQUS中的Submodel分析方法,将全局模型的计算结果以边界条件的形式传递给子模型,从而锈蚀对钢衬里撕裂的影响可直接通过子模型进行分析。
为简化计算,本文选取安全壳上远离贯穿件洞口和扶壁柱等奇异区的标准段为研究对象。同时,根据全局模型的计算结果,选择安全壳标准段上钢衬里产生最大应变的位置作为子模型研究区域。根据圣维南原理,考虑传递边界的影响,子模型尺寸取6 m×6 m。子模型各部件的建模方式、材料本构和单元属性等与全局模型保持一致。钢衬里锈蚀区域设置在子模型中心,其尺寸和形状参考文献[12]。为有效捕捉钢衬里锈蚀区的应变集中,需对其网格进行精细划分,子模型整体网格尺寸取200 mm,锈蚀区加密网格为8 mm,并在锈蚀区四周设置过渡区。子模型锈蚀区与网格划分如图11所示。
3.2.2 子模型有效性验证
在锈蚀模拟之前,需要验证子模型的有效性,一般的方法是通过对比子模型和全局模型相同区域的结果变量和云图分布来验证,如图12所示。
可以看出,子模型与全局模型钢衬里的应变分布规律基本一致;由于子模型最小网格尺寸为8 mm,远小于全局模型网格尺寸800 mm,因此子模型钢衬里应变略微偏大。结合应变计算结果和云图的对比,可认为子模型是有效的。
4 钢衬里撕裂准则与计算结果分析
4.1 锈蚀钢衬里撕裂准则
钢衬里的撕裂由其断裂应变决定,NRC在NUREG/CR-6706[11]和NUREG/CR-6920[12]报告中给出了有限元分析时考虑锈蚀的钢衬里撕裂准则,其表达式为:
{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} = {f_{\text{m}}}{f_{{\text{cor}}}}{f_{\text{g}}}{\varepsilon _{{\text{p}},{\text{eff}}}} (7) 式中:
{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} 为钢衬里的修正等效应变,当该值等于钢衬里单轴断裂应变{\varepsilon _{{\text{u0}}}} 时,钢衬里发生撕裂;{f_{{\text{cor}}}} 为锈蚀影响系数,未锈蚀时取1,锈蚀后NRC给的建议值如表2;{f_{\text{g}}} 为标距系数,该参数与模型复杂程度和网格尺寸有关;{\varepsilon _{{\text{p}},{\text{eff}}}} 为有限元计算的钢衬里等效应变;{f_{\text{m}}} 为多轴应力系数,计算式为:{f_{\text{m}}} = \frac{{1.0}}{{1.648{{\text{e}}^{ - ({\sigma _1} + {\sigma _2} + {\sigma _3})/2{\sigma _{{\text{vm}}}}}}}} (8) 式中:
{\sigma _1} 、{\sigma _2} 和{\sigma _3} 为主应力;{\sigma _{{\text{vm}}}} 为Mise应力。表 2 锈蚀影响系数Table 2. Corrosion influence coefficient参数 下限值 最佳估值 上限值 1/fcor 0.25 0.5 0.75 锈蚀钢衬里板的退化程度与锈蚀率有直接关系,因此锈蚀影响系数
{f_{{\text{cor}}}} 也应该与锈蚀率有关。按照NRC以折减锈蚀钢板断裂应变的方式来考虑锈蚀对钢板延性的影响,本文根据式(2)所得钢衬里板断裂应变与锈蚀率的退化规律,建立了新的锈蚀影响系数f_{{\text{cor}}}' 与锈蚀率的关系,如下式:f_{{\text{cor}}}'= \frac{1}{{M({\varepsilon _{\text{u}}})}} \quad\;\;\; (9) 进而本文提出的钢衬里撕裂准则如下:
{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} = {f_{\text{m}}}f_{{\text{cor}}}'{f_{\text{g}}}{\varepsilon _{{\text{p}},{\text{eff}}}} (10) 4.2 锈蚀钢衬里模拟方法及工况
NRC给出的锈蚀钢衬里模拟方法是以折减锈蚀区钢衬里的厚度,然后锈蚀区还是采用未锈蚀本构的方式[11-12]。此种模拟方式认为钢板除去锈蚀层后的基体材料性能与未锈蚀钢板一致,而本文试验结果表明,由于锈蚀的不均匀性,锈蚀钢板除去锈蚀层后的表面仍存在许多锈坑(如图3所示),受应力集中的影响会造成锈蚀钢板基体材料的屈服强度和极限强度等有明显退化,NRC模拟方法没有考虑到这一点。因此,本文钢衬里锈蚀模拟方式为,首先,根据锈蚀率折减锈蚀区钢衬里板的厚度,然后,根据式(3)赋予锈蚀区相应锈蚀率下的锈蚀本构关系。本文所用模拟方式同时考虑了锈蚀造成钢衬里截面损失和锈蚀钢衬里基体材料性能的退化,因此,更能接近实际锈蚀情况且计算更偏保守。
为研究不同锈蚀情况对安全壳钢衬里撕裂的影响,本文利用子模型考虑了钢衬里锈蚀率分别为0%、10%、20%、30%、40%和50%的6组锈蚀工况。同时,为对比本文锈蚀模拟方法与NRC方法的差异,按照NRC方法进行了6组同种工况模拟。钢衬里撕裂判断方式为:NRC方法和本文方法的锈蚀工况分别按照式(7)和式(10)进行判断。
4.3 计算结果分析
图13为按照本文模拟方法计算的钢衬里在不同锈蚀率下
{\varepsilon _{\text{p}}} 和{\varepsilon _{{\text{u0}}}} 的比值与内压的关系曲线({\varepsilon _{\text{p}}}/{\varepsilon _{{\text{u0}}}} = 1 时,钢衬里撕裂)。可以看出,随锈蚀率增大,钢衬里撕裂时的内压逐渐降低,且当锈蚀率为50%时,钢衬里撕裂时的内压较未锈蚀状态降低29.06%,表明锈蚀钢衬里容易在较低的事故压力下发生撕裂,从而导致安全壳提前发生密封失效。图14为按照NRC提出的模拟方法计算的不同锈蚀率下安全壳钢衬里应变与内压的关系,可以看出,锈蚀率越大,钢衬里应变增长速率越快,即在事故荷载下越容易发生撕裂。按照NUGRE-6920报告[12]和文献[9, 13-15]研究所述,锈蚀率为50%时,取
{f_{{\text{cor}}}}{\text{ = }}2 来判定钢衬里的撕裂,图15以该锈蚀率为例对比了本文方法与NRC方法计算的钢衬里应变与内压的关系。可以看出,内压较小时,本文方法和NRC方法计算的钢衬里应变基本一致,而当内压较大时,NRC方法高估了钢衬里撕裂时的应变和内压,因此锈蚀率比较大的情况下取{f_{{\text{cor}}}}{\text{ = }}2 判断钢衬里撕裂不够安全。本文按照NRC给出的锈蚀影响系数的三个限值,计算了不同锈蚀率下钢衬里撕裂时的内压,如图16所示。将按本文模拟方法得到的计算结果与其对比,可以看出:本文锈蚀模拟方法能很好地呈现不同锈蚀率下钢衬里的撕裂情况;对于NRC建议的三种锈蚀影响系数,在锈蚀率小于20%时,可以取上限值;当锈蚀率在20%~40%时,建议取最佳估值;当锈蚀率超过40%后,应当取下限值。
5 结论
本文通过锈蚀试验和数值模拟,对锈蚀钢衬里板的力学性能和锈蚀对安全壳钢衬里撕裂的影响进行了综合分析,得到以下结论:
(1) 锈蚀率在50%以内时,锈蚀对钢衬里板的弹性模量影响不大,但随锈蚀率增大,钢衬里板屈服平台逐渐变短甚至消失,其屈服强度、峰值强度、峰值应变和断裂应变大致呈线性退化规律,且锈蚀会造成钢衬里板的延性大幅降低。
(2) 本文建立的锈蚀钢衬里板的本构计算模型与试验结果吻合良好,本构模型可用于安全壳钢衬里锈蚀后的理论计算和数值模拟。
(3) 随锈蚀率增大,钢衬里发生撕裂时的内压逐渐降低,且当锈蚀率为50%时,撕裂时内压较未锈蚀状态降低29.06%,表明安全壳钢衬里锈蚀后容易在较低的事故压力下发生密封失效。
(4) 本文基于试验结果提出的钢衬里锈蚀模拟方法能直观反映不同锈蚀程度对钢衬里的影响,更能接近实际锈蚀情况。
(5) 为安全起见,对于NRC所建议的锈蚀影响系数,在锈蚀率小于20%时,可以取上限值,锈蚀率在20%~40%时,建议取最佳估值,而当锈蚀率超过40%后,应当取下限值。
-
表 1 钢衬里板拉伸试验结果
Table 1 Tensile test results of steel liner plate
试件组 弹性模量Es
平均值/MPa屈服强度fy
平均值/MPa峰值强度fp
平均值/MPa峰值应变ɛp
平均值断裂应变ɛu
平均值L-0% 203 958 310.57 431.14 0.2657 0.4363 L-10% 201 631 290.42 394.12 0.2105 0.3009 L-20% 202 142 264.10 379.22 0.1792 0.2414 L-30% 200 109 267.21 364.65 0.1425 0.1935 L-40% 201 966 248.34 361.25 0.1413 0.1899 L-50% 199 694 231.02 335.07 0.1095 0.1464 注:以上各强度值为试件锈蚀后的荷载除以锈蚀后的截面面积;部分试件断裂不在测量标距内,相应的数据已舍去。 表 2 锈蚀影响系数
Table 2 Corrosion influence coefficient
参数 下限值 最佳估值 上限值 1/fcor 0.25 0.5 0.75 -
[1] 金松, 李鑫波, 贡金鑫. 严重事故下核电厂安全壳结构概率性能评价[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(6): 103 − 112. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0437 JIN Song, LI Xinbo, GONG Jinxin. Probabilistic performance evaluation of nuclear containment structure subjected to severe accidents [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(6): 103 − 112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0437
[2] 朱升冬, 陈国兴, 蒋鹏程, 等. 松软场地上桩筏基础AP1000核岛结构的三维非线性地震反应特性[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(1): 129 − 142. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.02.0121 ZHU Shengdong, CHEN Guoxing, JIANG Pengcheng, et al. 3D nonlinear response characteristics of the pile-raft-supported AP1000 nuclear island building in soft deposits subjected to strong ground motions [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(1): 129 − 142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.02.0121
[3] PETR B, ALENA K. An estimation of the effect of steel liner on the ultimate bearing capacity of prestressed concrete containment [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2018, 328: 197 − 208. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2017.12.026
[4] DUNN D S, PULVIRENTI A L, HISER M A. Containment steel liner corrosion operating experience summary technical letter report-revision 1 [R]. Washington: NRC, 2011.
[5] 贡金鑫, 万广泽, 郭俊营, 等. 核电站安全壳老化研究状况及进展[J]. 工业建筑, 2017, 47(1): 1 − 9, 32. GONG Jinxin, WAN Guangze, GUO Junying, et al. State of the art studies of containment ageing of NPP [J]. Industrial Construction, 2017, 47(1): 1 − 9, 32. (in Chinese)
[6] HESSHEIMER M F, DAMERON R A. Containment integrity research at sandia national laboratories [R]. Washington: NRC, NUREG/CR-6906, 2006.
[7] HANSON N W, SCHULTZ D M, ROLLER J J, et al. Testing of large-scale concrete containment structural elements [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1987, 100(2): 129 − 149. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(87)90039-2
[8] HANSON N W, SCHULTZ D M, ROLLER J J, et al. Results of large-scale test of discontinuity region in a prestressed concrete containment [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1987, 104(3): 321 − 328. doi: 10.1016/0029-5493(87)90210-X
[9] PETTI J P, SPENCER B W, GRAVES H L. Risk-informed assessment of degraded containment vessels [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008, 238(8): 2038 − 2047. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2007.10.025
[10] CHERRY J L. Analyses of containment structures with corrosion damage [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, SAND96-0004C, 1999.
[11] CHERRY J L, SMITH J A. Capacity of steel and concrete containment vessels with corrosion damage [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, NUREG/CR-6706, 2001.
[12] SPENCER B W, PETTI J P, KUNSMAN D M. Risk-Informed Assessment of Degraded Containment Vessels [R]. Washington: NRC, NUREG/CR-6920, 2006.
[13] SMITH J A, CHERRY J L. Analyses of a Reinforced Concrete Containment with Steel liner Corrosion Damage [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, NM87185-0744, 1999.
[14] PETTI J P, SPENCER B W. Risk-informed assessment of degraded containment vessels [C]// Proceedings of ICONE14 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering. Miami Florida, USA, ASME, 2006.
[15] PETTI J P, KALINICH D A, JUN J, et al. Effects of steel liner degradation on the severe accident consequences at a PWR plant with a reinforced concrete containment [C]// Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology. Espoo Finland, SMiRT, 2009.
[16] ALHANAEE S, YI Y, SCHIFFER A. Ultimate pressure capacity of nuclear reactor containment buildings under unaged and aged conditions [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2018, 335: 128 − 139. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2018.05.017
[17] BRUNEAU M, ZAHRAI S M. Effect of severe corrosion on cyclic ductility of steel [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1997, 123(11): 1478 − 1486. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1997)123:11(1478)
[18] BS EN 10028-2: 2017, Flat products made of steels for pressure purposes - Part 2: Non-alloy and alloy steels with specified elevated temperature properties [S]. European Standards Institute, 2017.
[19] GB/T 228. 1−2010, 金属材料拉伸试验第1部分: 室温试验方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010. GB/T 228. 1−2010, Metallic materials tensile testing part 1: method of test at room temperature [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2010. (in Chinese)
[20] ERLER B A, WEYERS R E, SAGUES A, et al. Nuclear containment steel liner corrosion workshop: final summary and recommendation report [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, SAND2010-8718, 2011.
[21] FENG W, DONG Z, LIU W, et al. An experimental study on the influence of applied voltage on current efficiency of rebars with a modified accelerated corrosion test [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 122: 104120. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104120
[22] GB/T 16545−2015, 金属和合金的腐蚀-腐蚀试样上腐蚀产物的清除[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. GB/T 16545−2015, Corrosion of metals and alloys – removal of corrosion products form corrosion test specimens [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015. (in Chinese)
[23] 张伟平, 商登峰, 顾祥林. 锈蚀钢筋应力-应变关系研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(5): 586 − 592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.05.004 ZHANG Weiping, SHANG Dengfeng, GU Xianglin. Stress-strain relationship of corroded steel bars [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2006, 34(5): 586 − 592. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.05.004
[24] 龚帆, 齐盛珂, 邹易清, 等. 锈蚀高强钢丝力学性能退化的试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(10): 105 − 115. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.11.0669 GONG Fan, QI Shengke, ZOU Yiqing, et al. Experimental study on degradation of mechanical properties of corroded high strength steel wire [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(10): 105 − 115. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.11.0669
[25] 徐善华, 王皓, 苏磊, 等. 考虑点蚀损伤的锈蚀钢板延性退化[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(6): 1257 − 1263. XU Shanhua, WANG Hao, SU Lei, et al. Ductility degradation of corroded steel plates with pitting damage [J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1257 − 1263. (in Chinese)
[26] SHOKOOHFAR A, RAHAI A. Nonlinear analysis of prestressed concrete containment vessel (PCCV) using the damage plasticity model [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2016, 298: 41 − 50. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2015.12.019
[27] SAENZ L P. Equation for Stress-Strain Curve of Concrete by Desai P and Krishnan S [J]. American Concrete Institute Journal, 1964, 61: 1229 − 1235.
[28] JIN S, LI Z C, DONG Z F, et al. A simplified fragility analysis methodology for containment structure subjected to overpressure condition [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2020, 184: 104104. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2020.104104
[29] HU H T, SCHNOBRICH W C, Nonlinear finite element analysis of reinforced concrete plates and shells under monotonic loading [J]. Computers and Structures, 1991, 38: 637 - 651.
[30] ZHANG C Y, CHEN P, ZHANG J H, et al. Evaluation of the structural integrity of the CPR1000 PWR containment under steam explosion accidents [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2014, 278: 632 − 643. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2014.08.019
[31] TONG L, ZHOU X, CAO X. Ultimate pressure bearing capacity analysis for the prestressed concrete containment [J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2018, 121: 582 − 593. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2018.08.020
[32] JIN S, GONG J X. Fragility analysis and probabilistic performance evaluation of nuclear containment structure subjected to internal pressure [J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2021, 208: 107400. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107400
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李鑫波,贡金鑫. 核安全壳在钢衬里锈蚀情况下的概率安全分析. 哈尔滨工程大学学报. 2024(12): 2281-2289 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: