STUDY ON THE CONSOLIDATION BEHAVIORS OF MULTI-REINFORCEMENT COMPOSITE FOUNDATION CONSIDERING TIME-DEPENDENT WELL RESISTANCE
-
摘要:
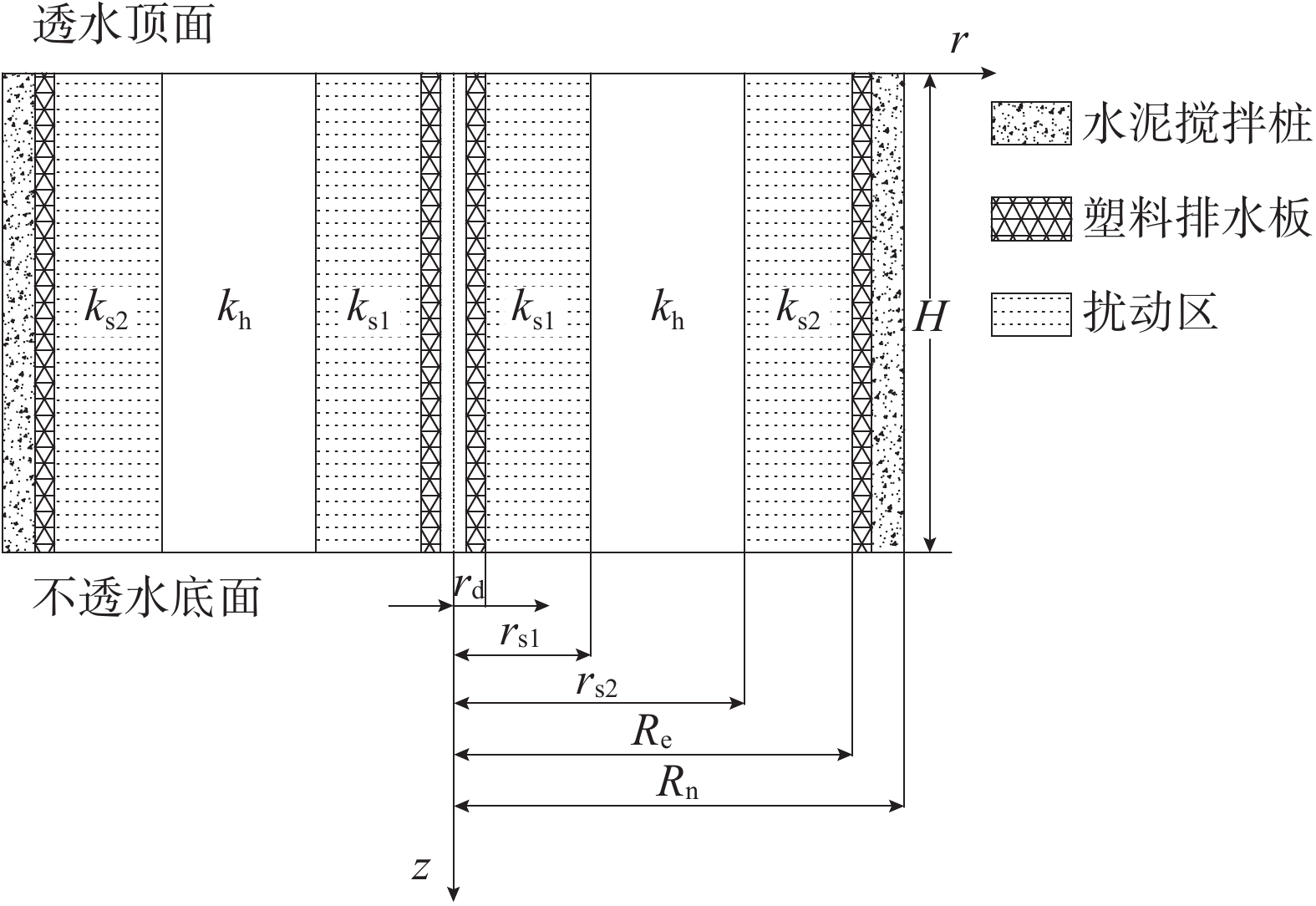
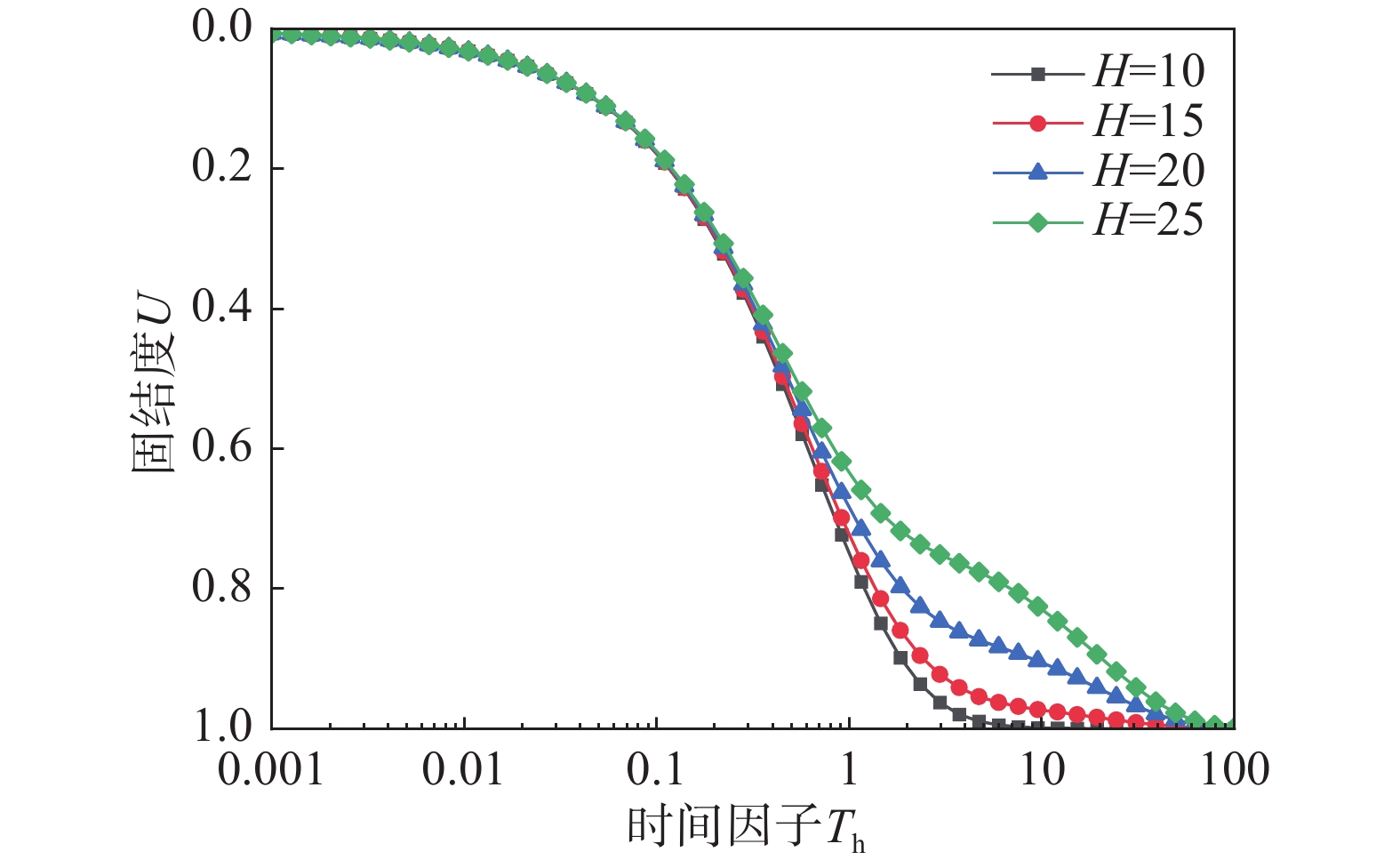
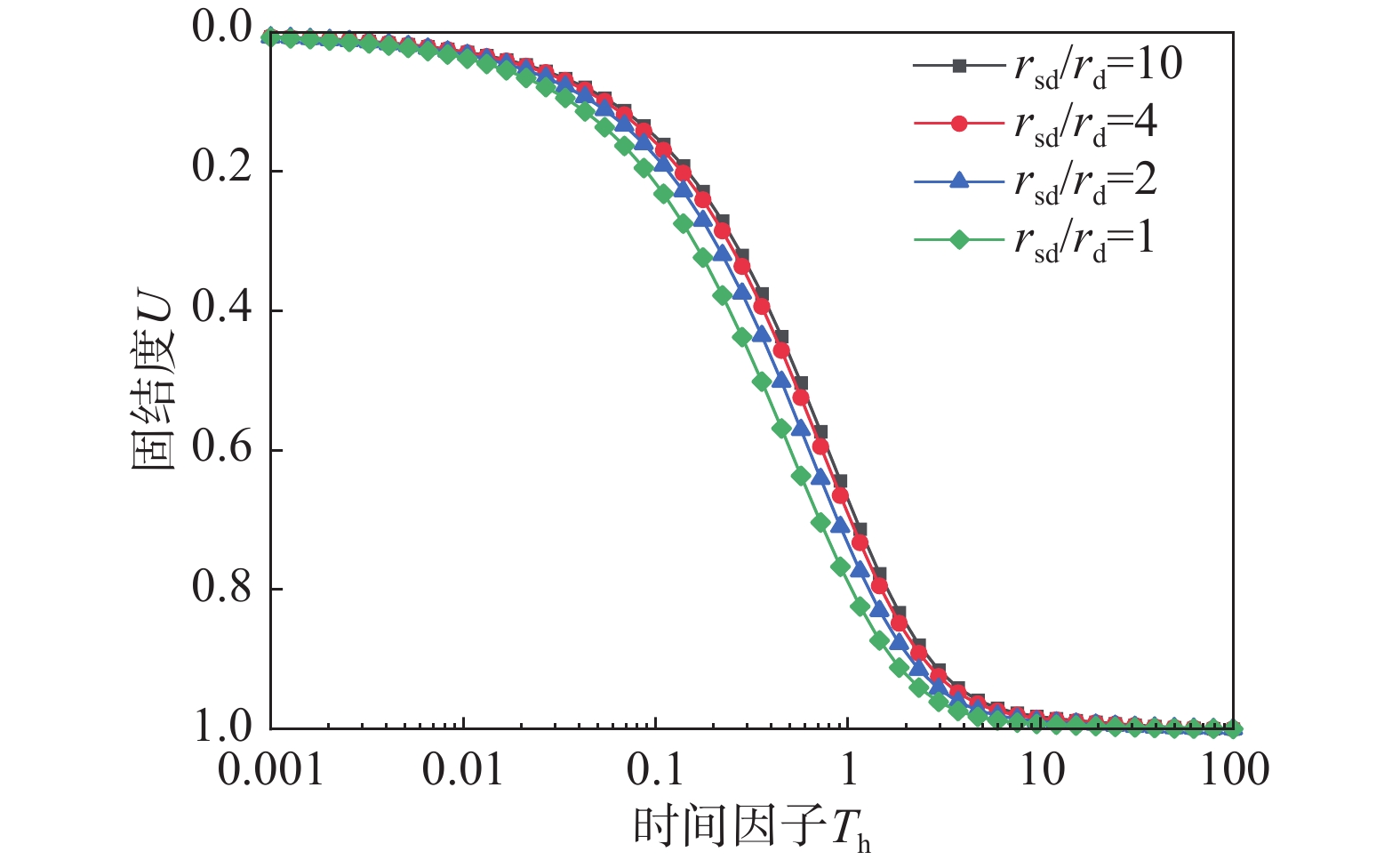
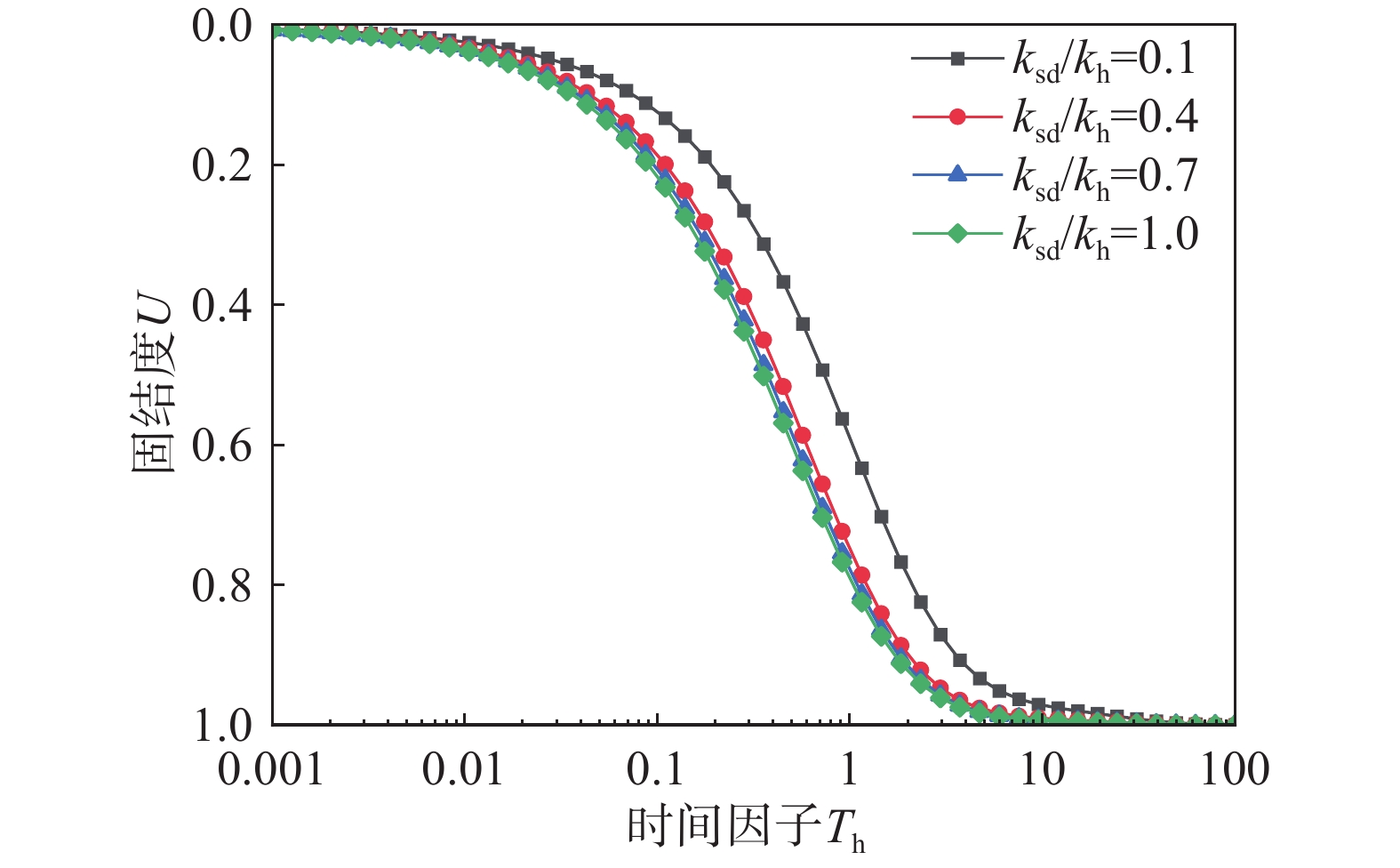
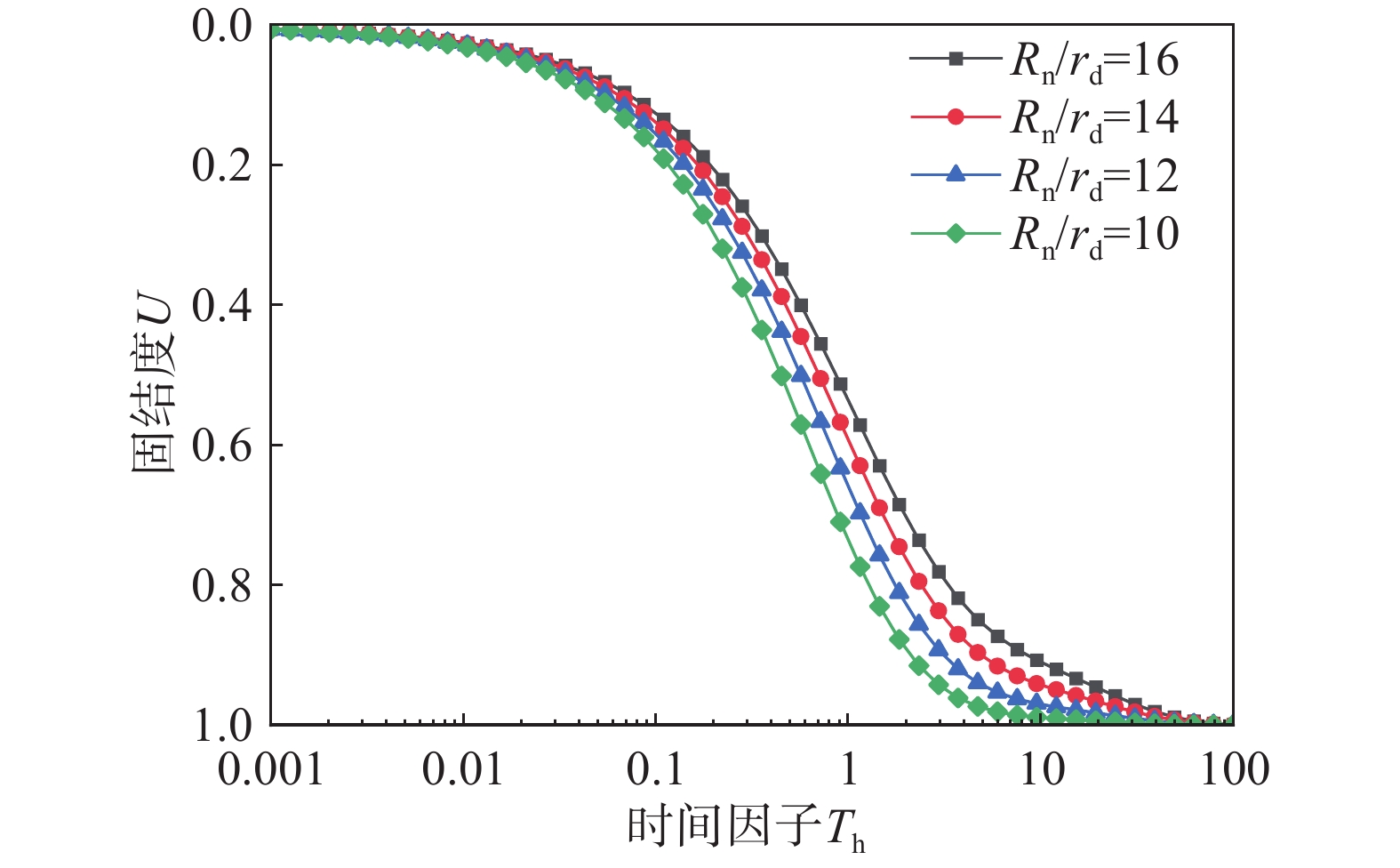
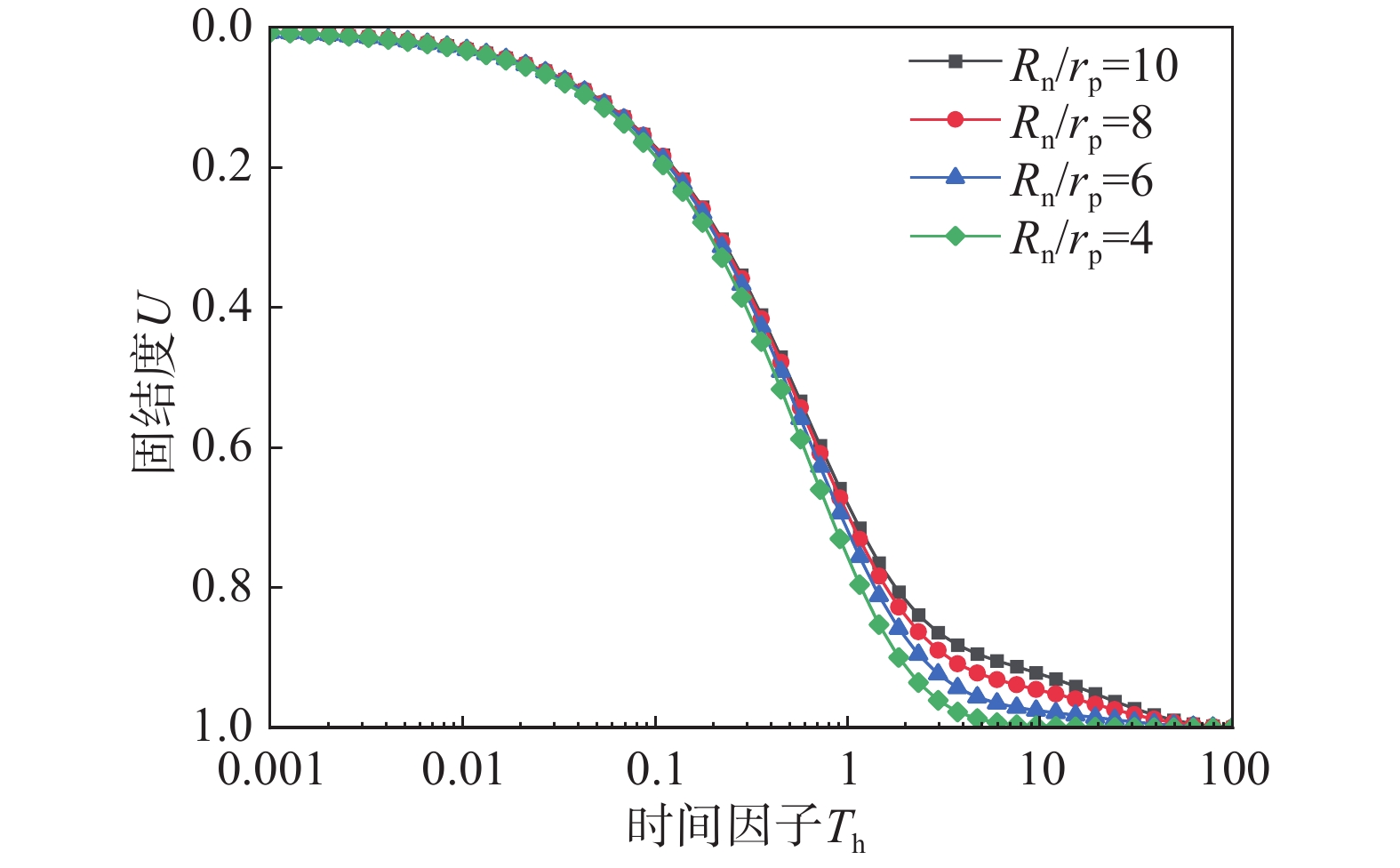
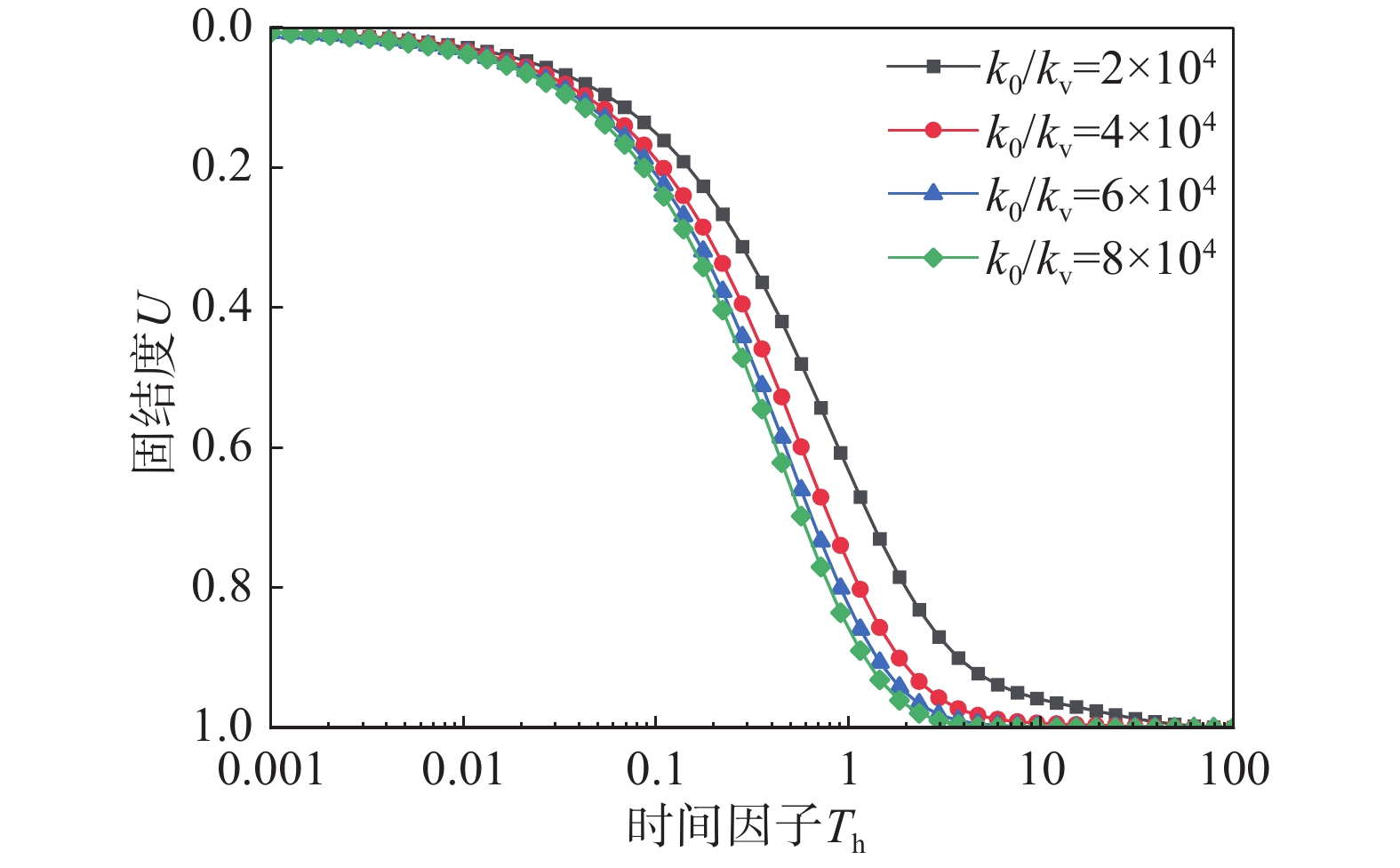
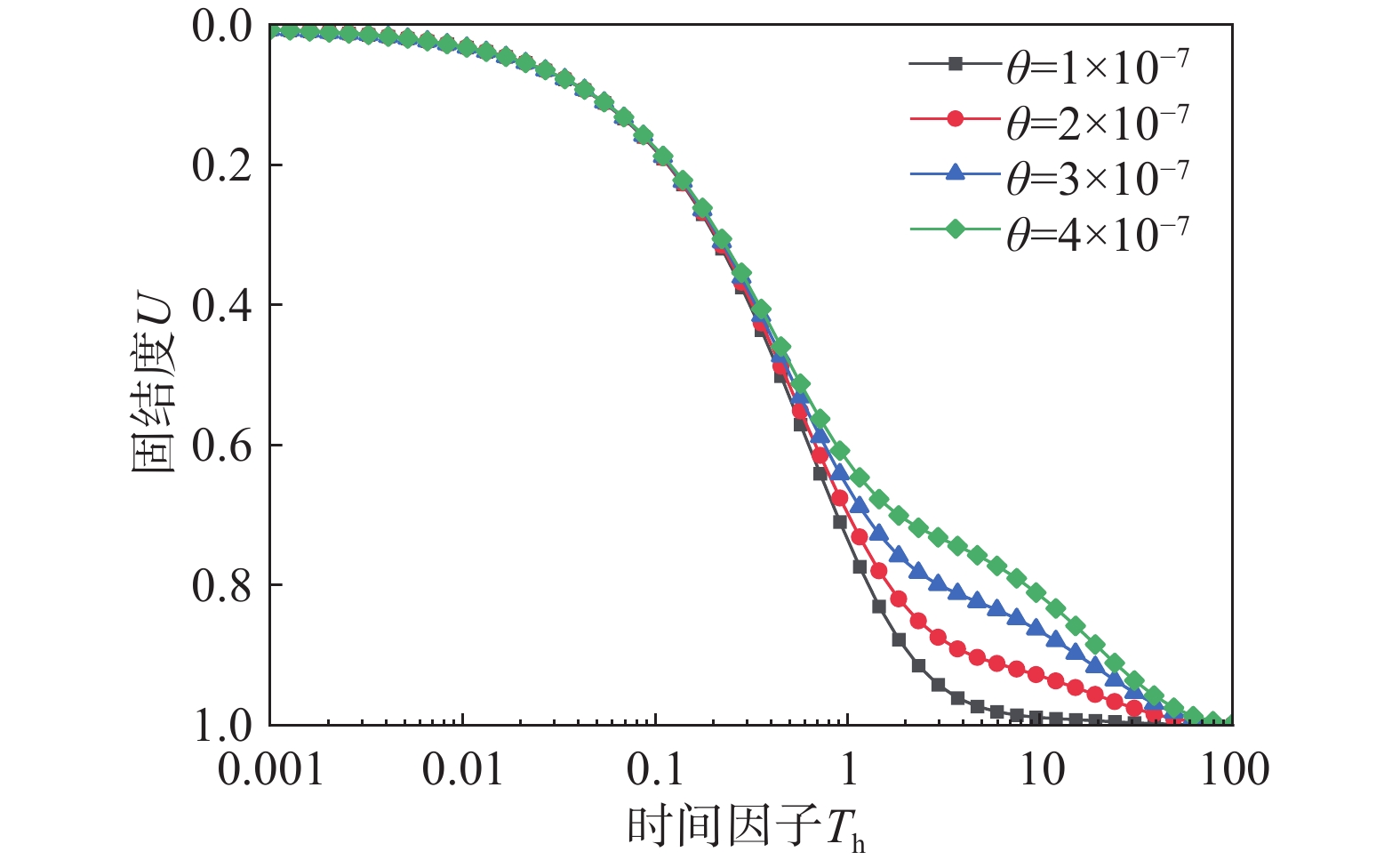
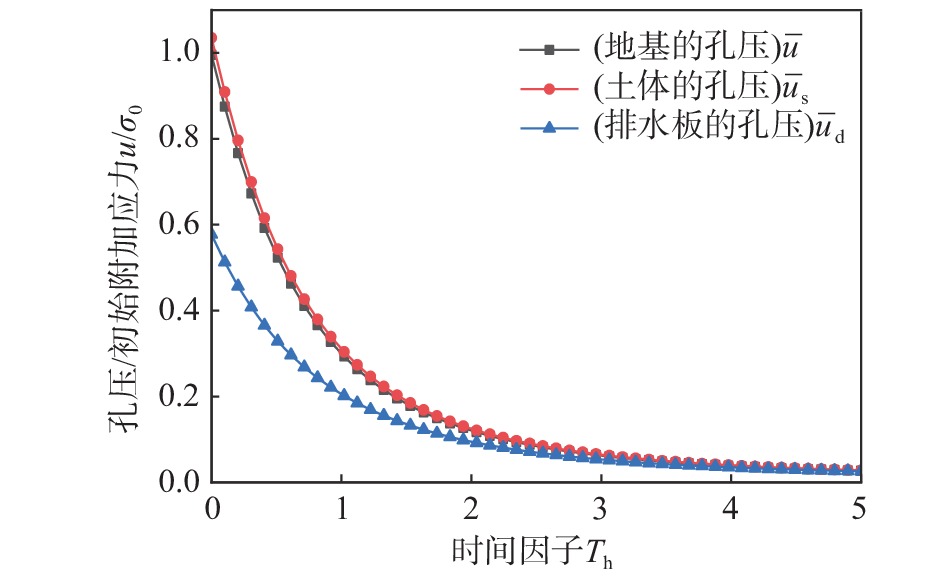
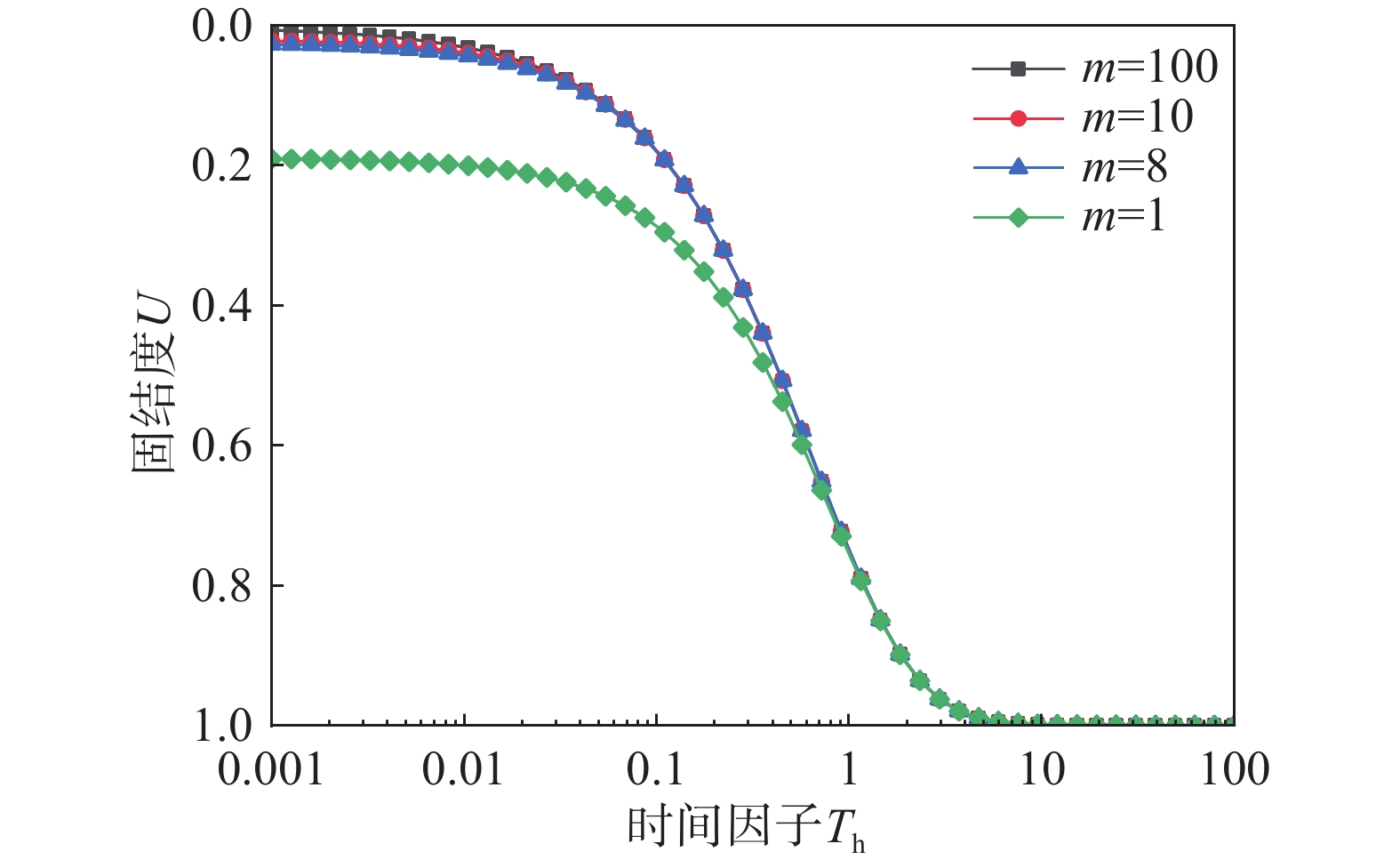
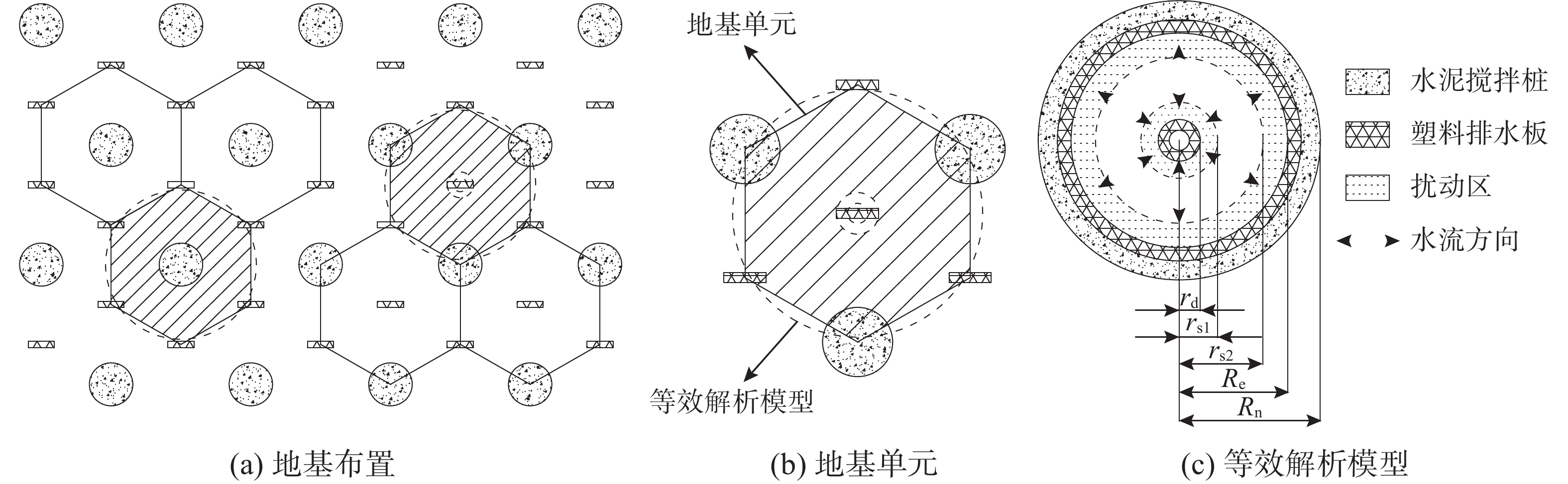
该文以塑料排水板联合水泥搅拌桩多元复合地基为研究对象,通过假定排水板的渗透系数随时间呈指数型衰减,考虑了排水板在固结过程中的淤堵效应对地基固结性状的影响。同时,该文还考虑排水板的涂抹效应、水泥搅拌桩的扰动效应以及土体的径-竖向耦合渗流,推导得出多元复合地基的固结控制方程及其解答。通过与已有解答和现场试验的对比分析,验证该文解答的正确性。最后,采用参数敏感性分析法对多元复合地基固结性状进行研究。研究结果表明:复合地基井阻因子θ对固结后期影响较大,当θ值较大时,径向渗流由于排水板的淤堵效应将提前终止,最终仅由竖向渗流使得地基达到完全固结;初始渗透系数k0越大,井阻因子θ越小,涂抹作用越弱,板和桩的置换率越高,复合地基固结速率就越快。
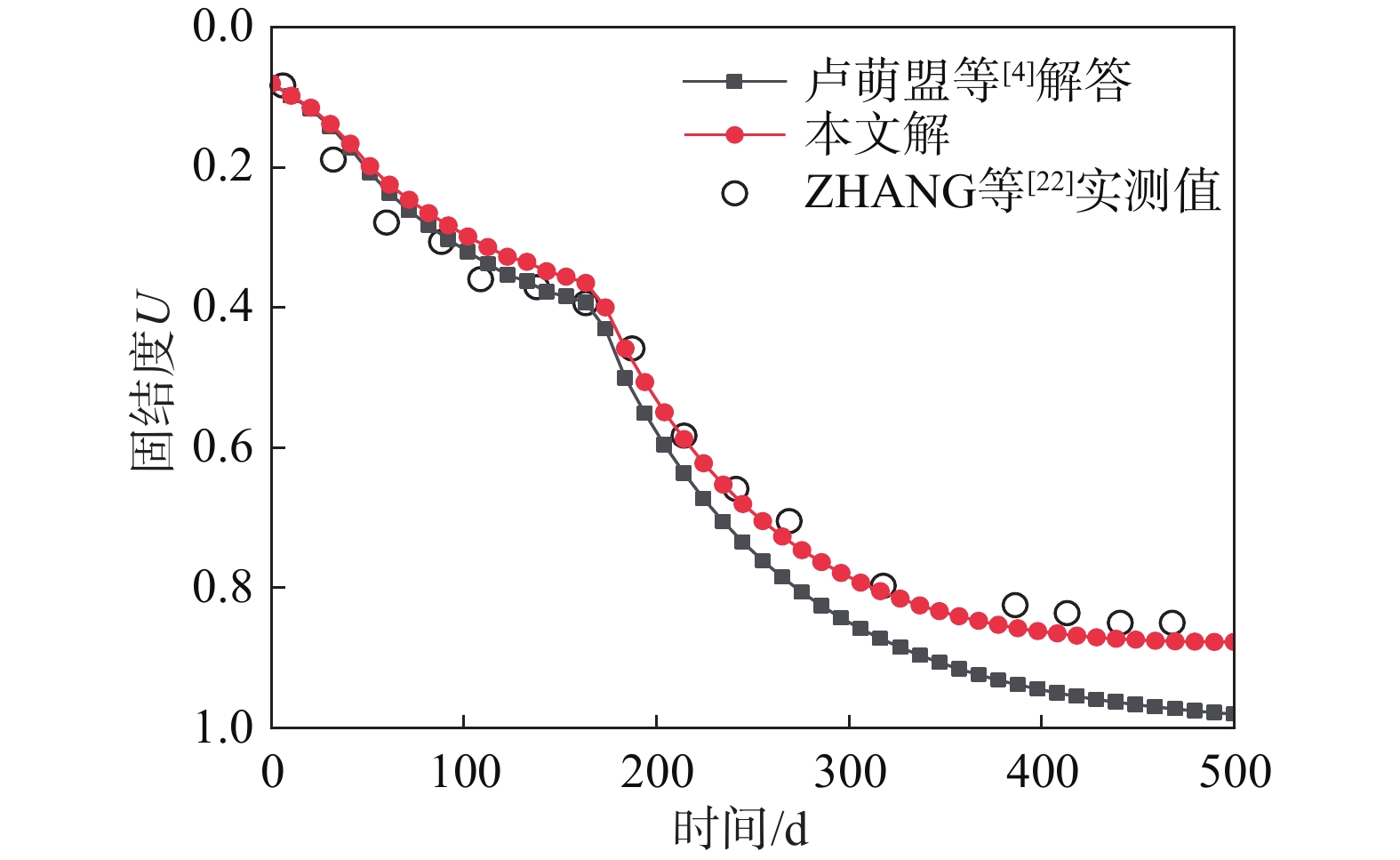
Abstract:This paper studies the multi-reinforcement composite foundation improved by prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs) with cement mixing piles, and the influence of clogging effect of PVDs is considered by assuming the permeability coefficient of PVDs decays exponentially with time. In addition, the smear effect of PVDs, the disturbance effect of the cement mixing pile, and the coupled radial-vertical flow within the soil are considered. The governing equations of consolidation of the multi-reinforcement composite foundation and the corresponding solutions are derived. The solutions is verified by comparison with several existing solutions and three field tests. Finally, the consolidation behavior of the multi-reinforcement composite ground is analyzed by a series of parametrical analysis. The results show the well resistance factor θ has a great influence on the later stage of consolidation process. A large value for θ will result in the radial flow ceasing in advance. Consequently, the consolidation will be completed only via the vertical flow. The following factors will lead to a faster consolidation rate, including a larger value of the initial permeability coefficient k0, a smaller value for the well resistance factor θ, weaker smearing effect, and larger replacement ratios of PVDs and piles.
-
-
表 1 模型参数取值表
Table 1 The parameters in calculation
参数 取值 参数 取值 H/m 13 kv/(×10−9 m/s) 1.63 H/Rn 10 kh/kv 2 Rn/rd 39.4 k0/(×10−5 m/s) 5.5 Rn/rp 5.2 Es/MPa 1.68 rsd/rd 2 Ep/Es 50 rsp/rp 3 Ed/Es 1 ksd/kh 1/3 σ0/kPa 10 ksp/kh 0.3 θ/(×10−7 s−1) 1 表 2 模型参数取值表
Table 2 The parameters in calculation
参数 取值 参数 取值 H/m 13.0 kh/kv 2 Rn/m 1.155 kh/ksd 3 Rn/rd 39.4 kd/kh 104 Rn/rp 5.2 Es/MPa 1.68 rsd/rd 3 Ep/Es 7 kv/(×10−9 m/s) 1.63 − − 表 3 模型参数取值表
Table 3 The values of the parameters in calculation
参数 取值 参数 取值 H/m 10.5 kh/kv 2 Rn/m 1.039 kh/ksd 3 Rn/rd 39.4 kd/(×10−6 m3/s) 35 Rn/rp 5.2 Es/MPa 1.25 rsd/rd 3 Ep/Es 9.4 kv/(×10−9 m/s) 1.61 − − 表 4 模型参数取值表
Table 4 The values of the parameters in calculation
参数 复合层取值 固结层取值 参数 复合层取值 固结层取值 H/m 10 10 kh/kv 4.7 2.0 Rn/m 1.44 2.50 kh/ksd 3 3 Rn/rd 39.4 39.4 kd/kh 104 1.5×104 Rn/rp 5.2 − Es/MPa 10.4 7.4 rsd/rd 3 3 Ep/Es 2.9 4.1 kv/(×10−9 m/s) 2.38 1.77 − − − -
[1] 郑俊杰, 区剑华, 吴世明, 等. 多元复合地基的理论与实践[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2002, 24(2): 208 − 212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.02.018 ZHENG Junjie, OU Jianhua, WU Shiming, et al. Theory and practice of multi-element composite ground [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2002, 24(2): 208 − 212. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2002.02.018
[2] 郑刚, 龚晓南, 谢永利, 等. 地基处理技术发展综述[J]. 土木工程学报, 2012, 45(2): 127 − 146. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.02.023 ZHENG Gang, GONG Xiaonan, XIE Yongli, et al. State-of-the-art techniques for ground improvement in China [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2012, 45(2): 127 − 146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.02.023
[3] 龚晓南. 复合地基理论及工程应用(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018: 430 − 431. GONG Xiaonan. Composite foundation theory and engineering application (third edition)[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018: 430 − 431. (in Chinese)
[4] 卢萌盟, 白垚, 李红军, 等. 多元组合桩复合地基固结解析模型与解答[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(增刊 2): 3301 − 3312. LU Mengmeng, BAI Yao, LI Hongjun, et al. Analytical models and solutions for consolidation of composite foundation with multiple types of reinforcements [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(Suppl 2): 3301 − 3312. (in Chinese)
[5] BARRON R A. Consolidation of fine-grained soils by drain wells by drain wells [J]. Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, 1948, 113(1): 718 − 742. doi: 10.1061/TACEAT.0006098
[6] HANSBO S. Consolidation of fine-grained soils by prefabricated drains [C]// Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Stockholm, 1981: 677 − 682.
[7] HANSBO S, JAMIOLKOWSKI M, KOK L. Consolidation by vertical drains [J]. Géotechnique, 1981, 31(1): 45 − 66.
[8] 谢康和, 曾国熙. 等应变条件下的砂井地基固结解析理论[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1989, 11(2): 3 − 17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1989.02.002 XIE Kanghe, ZENG Guoxi. Consolidation theories for drain wells under equal strain condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1989, 11(2): 3 − 17. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1989.02.002
[9] 郭彪, 韩颖, 龚晓南, 等. 随时间任意变化荷载下砂井地基固结分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(6): 2369 − 2377. GUO Biao, HAN Ying, GONG Xiaonan, et al. Consolidation analysis with vertical drains and general time-dependent loading [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(6): 2369 − 2377. (in Chinese)
[10] LU M M, WANG S Y, SLOAN S W, et al. Nonlinear radial consolidation of vertical drains under a general time-variable loading [J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2015, 39(1): 51 − 62. doi: 10.1002/nag.2295
[11] LU M M, LI D X, JING H W, et al. Analytical solution for consolidation of band-shaped drain based on an equivalent annular drain [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 19(6): 04019043. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001423
[12] DENG Y B, XIE K H, LU M M, et al. Consolidation by prefabricated vertical drains considering the time dependent well resistance [J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2013, 36: 20 − 26. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2012.10.003
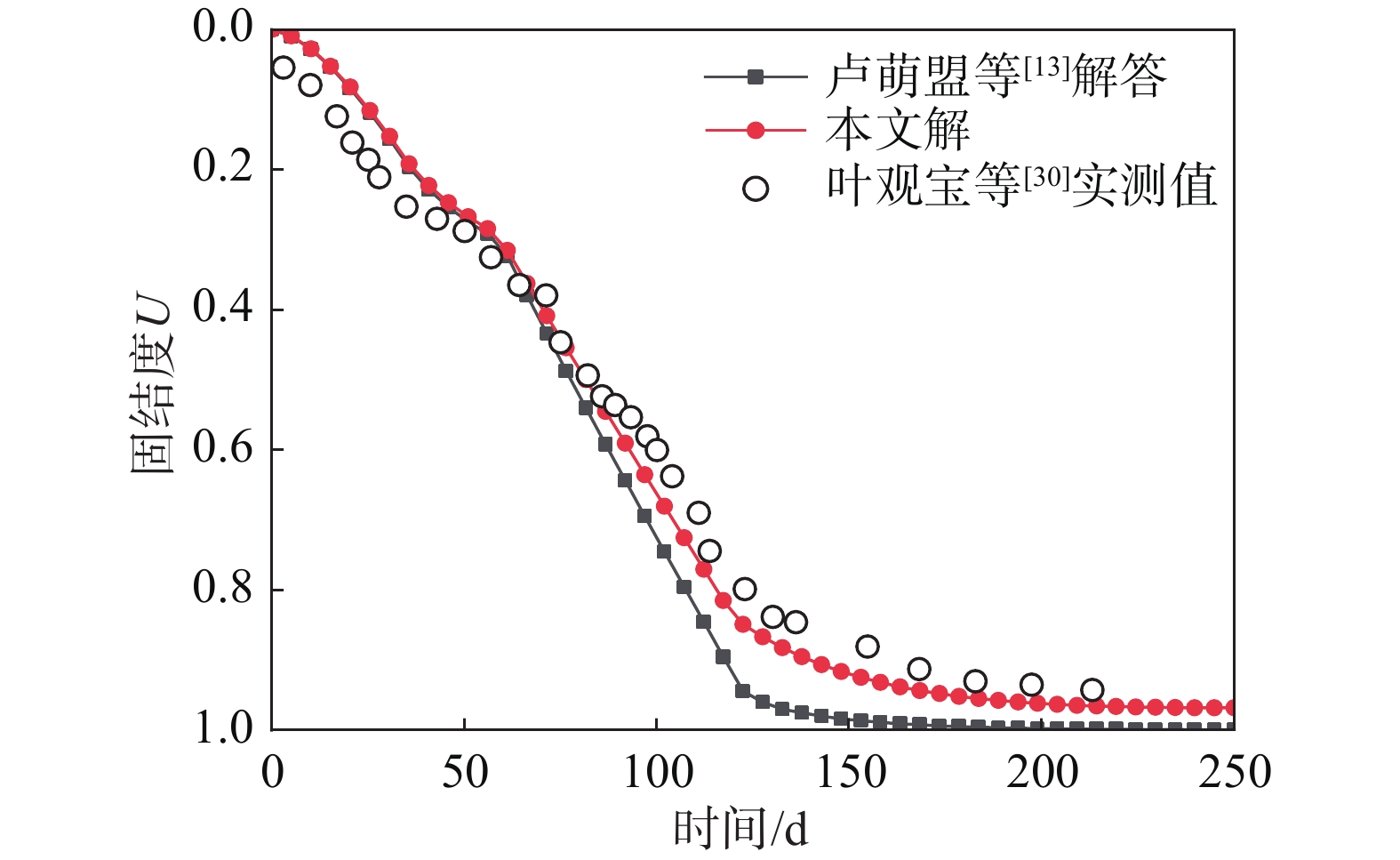
[13] 江文豪, 詹良通, 杨策, 等. 考虑井阻随时间变化及径-竖向渗流下砂井地基固结的解析解及其分析[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(6): 218 − 226, 256. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0478 JIANG Wenhao, ZHAN Liangtong, YANG Ce, et al. Analytical solution and analysis for consolidation of sand−drained ground considering the time-dependent well resistance and radial-vertical flow [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(6): 218 − 226, 256. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0478
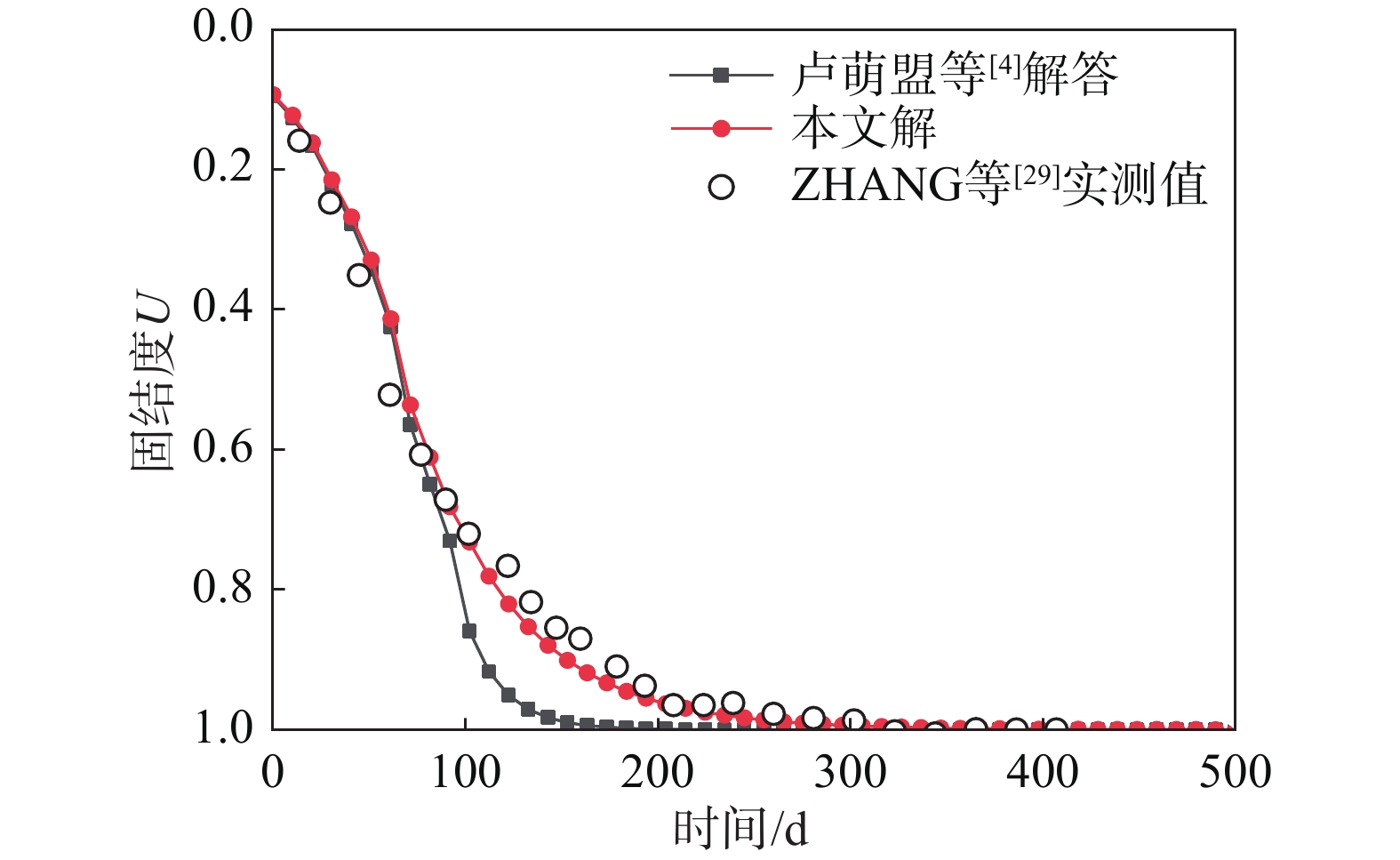
[14] 江文豪, 詹良通. 真空联合堆载预压下基于指数形式渗流的砂井地基非线性固结解[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(2): 69 − 76, 133. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.03.0190 JIANG Wenhao, ZHAN Liangtong. Analytical solution for nonlinear consolidation of sand-drained ground with exponential flow under vacuum combined surcharge preloading [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(2): 69 − 76, 133. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.03.0190
[15] 冯霞, 宗梦繁, 田乙, 等. 考虑边界排水时间效应的软土一维非线性固结近似解答[J]. 工程力学, 2023, 40(1): 100 − 110. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.07.0575 FENG Xia, ZONG Meng-fan, TIAN Yi, et al. Approximate solution for one-dimensional nonlinear consolidation theory of soil considering the time effect of boundary drainage [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2023, 40(1): 100 − 110. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.07.0575
[16] NGUYEN B P, KIM Y T. Radial consolidation of PVD-installed normally consolidated soil with discharge capacity reduction using large-strain theory [J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2019, 47(2): 243 − 254. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2019.01.008
[17] 卢萌盟, 张强, 靖洪文, 等. 基于环形等效的排水板地基固结[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(2): 513 − 520. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1009 LU Mengmeng, ZHANG Qiang, JING Hongwen, et al. Consolidation of band-shaped drain based on equivalent annular drain [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(2): 513 − 520. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1009
[18] 谢康和, 泮秋元, 施淑群, 等. 一种计算搅拌桩复合地基固结沉降的方法[C]//岩土力学数值方法的工程应用——第二届全国岩石力学数值计算与模型实验学术研讨会论文集. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1990: 404 − 409. XIE Kanghe, PAN Qiuyuan, SHI Shuqun, et al. A method for calculating consolidation settlement of mixed pile composite ground [C]// Engineering Application of Numerical Methods in Geotechnical Mechanics-Proceedings of the 2nd National Symposium on Numerical Calculation and Model Experiments of Rock Mechanics. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 1990: 404 − 409. (in Chinese)
[19] TERZAGHI K. Theoretical soil mechanics [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1943: 265 − 296.
[20] 杨涛, 李国维. 路堤荷载下不排水端承桩复合地基固结分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(12): 1831 − 1836. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.12.014 YANG Tao, LI Guowei. Consolidation analysis of composite ground with undrained penetrating piles under embankment load [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(12): 1831 − 1836. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.12.014
[21] 卢萌盟, 谢康和, 周国庆, 等. 不排水桩复合地基固结解析解[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(4): 574 − 579. LU Mengmeng, XIE Kanghe, ZHOU Guoqing, et al. Analytical solution for consolidation of composite ground with impervious pile [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(4): 574 − 579. (in Chinese)
[22] ZHANG D W, LIU S Y, HONG Z S. Consolidation calculating method of soft ground improved by DJM-PVD combined method [C]// Proceedings of the Geoshanghai International Conference 2006. Shanghai: ASCE, 2006: 29 − 36.
[23] 陈蕾, 刘松玉, 洪振舜. 排水粉喷桩复合地基固结计算方法的探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(2): 198 − 203. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.02.008 CHEN Lei, LIU Songyu, HONG Zhenshun, et al. Study of consolidation calculation of soft ground improved by dry jet mixing combined with vertical drain method [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(2): 198 − 203. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.02.008
[24] 刘吉福. 路堤下等应变复合地基的固结分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(增刊 1): 3042 − 3050. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.z1.067 LIU Jifu. Analysis of consolidation of equal-strain composite ground under embankment [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(Suppl 1): 3042 − 3050. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.z1.067
[25] YE G B, ZHANG Z, XING H F, et al. Consolidation of a composite foundation with soil-cement columns and prefabricated vertical drains [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2012, 71(1): 87 − 98. doi: 10.1007/s10064-011-0354-y
[26] 杨涛, 李超. 刚性基础下组合渗流碎石桩-不排水桩复合地基固结分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(11): 2631 − 2640. YANG Tao, LI Chao. Consolidation analysis of stone column-impervious pile composite ground underneath rigid foundation considering radial and vertical flows within stone columns [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(11): 2631 − 2640. (in Chinese)
[27] LU M M, JING H W, ZHOU Y, et al. General analytical model for consolidation of stone column-reinforced ground and combined composite ground [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(6): 04016131. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000836
[28] ZHANG Y G, XIE K H, WANG Z. Consolidation analysis of composite ground improved by granular columns considering variation of permeability coefficient of soil [C]// Proceedings of the Geoshanghai International Conference 2006. Shanghai, China: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2006: 135 − 142.
[29] ZHANG D W, LIU S Y, HAN W J, et al. A combined dry jet mixing-prefabricated vertical drain method for soft ground improvement: A case study [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2013, 31(4): 332 − 347.
[30] 叶观宝, 陈健, 邢皓枫, 等. 长板-短桩组合型复合地基固结特性试验[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(12): 1725 − 1729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2010.12.002 YE Guanbao, CHEN Jian, XING Haofeng, et al. In-situ tests on consolidation of composite foundation composed of short cement-soil piles and long plastic drainage plates [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2010, 38(12): 1725 − 1729. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2010.12.002
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 许宝龙,卢萌盟,刘元杰,张鑫岩. 多元排水体复合地基固结解析模型和解答. 岩土力学. 2024(S1): 73-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: