SOLUTION AND DETERMINATION OF OVERLYING PIPE-SOIL VOID RANGE INDUCED BY SHALLOW TUNNEL EXCAVATION
-
摘要:
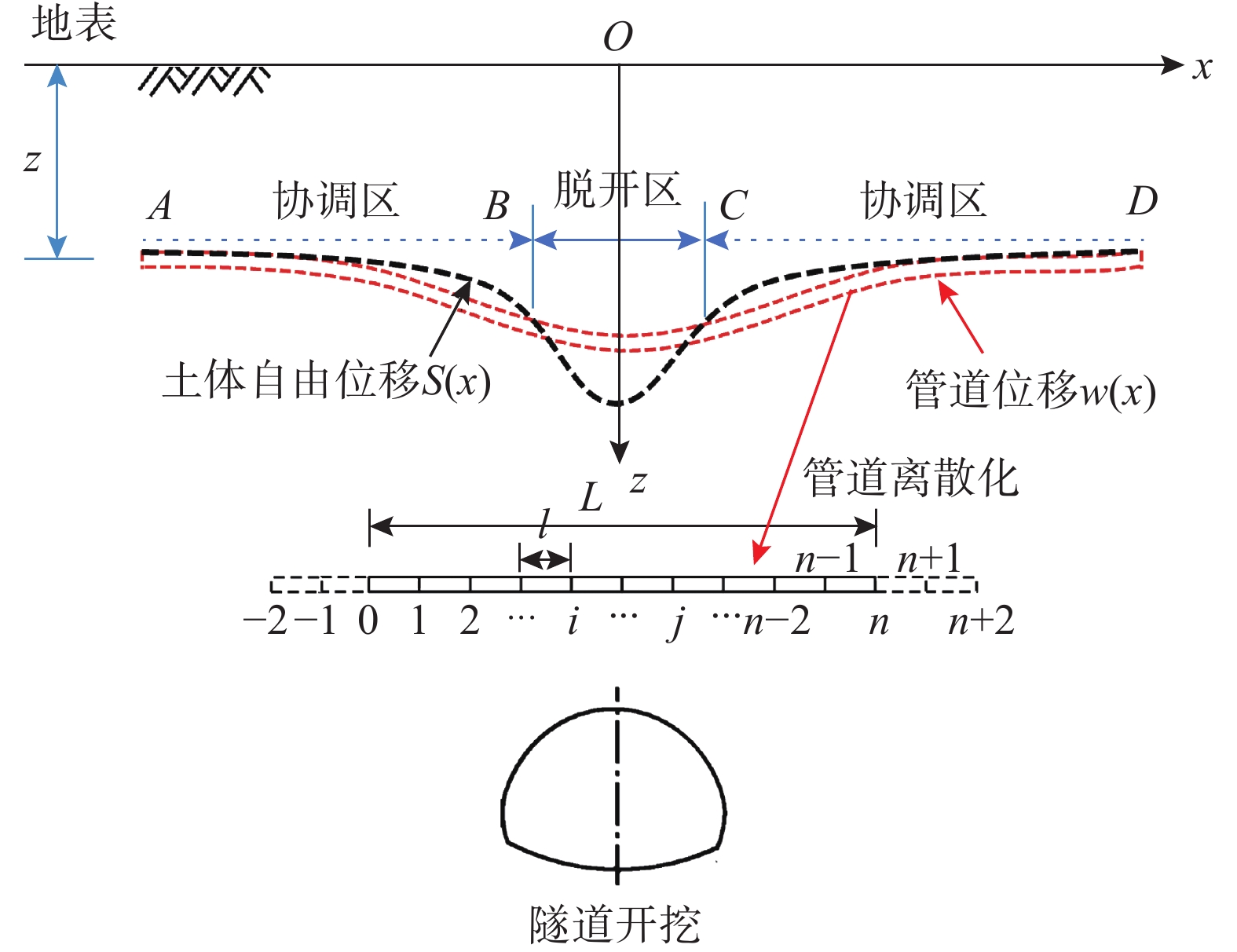
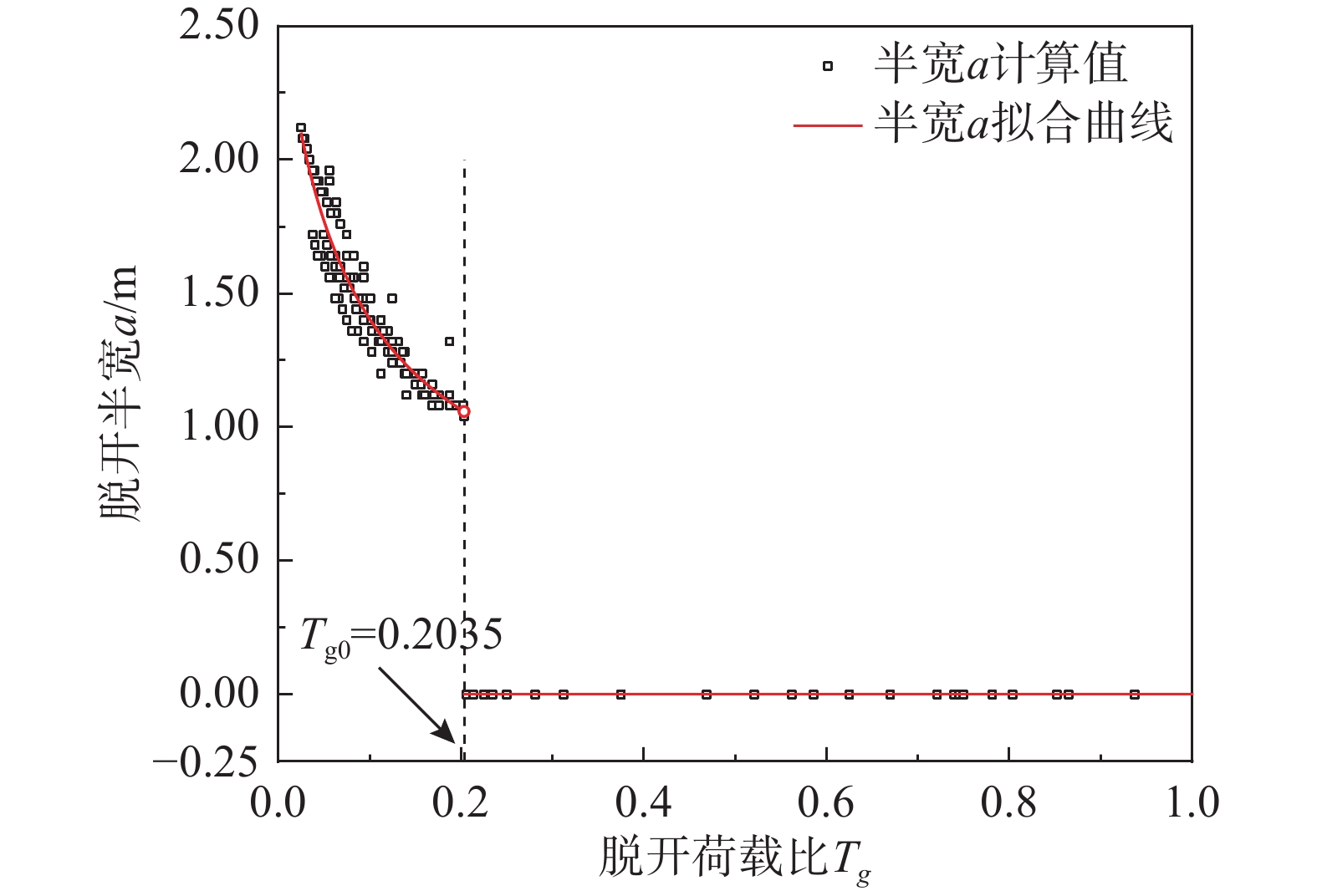
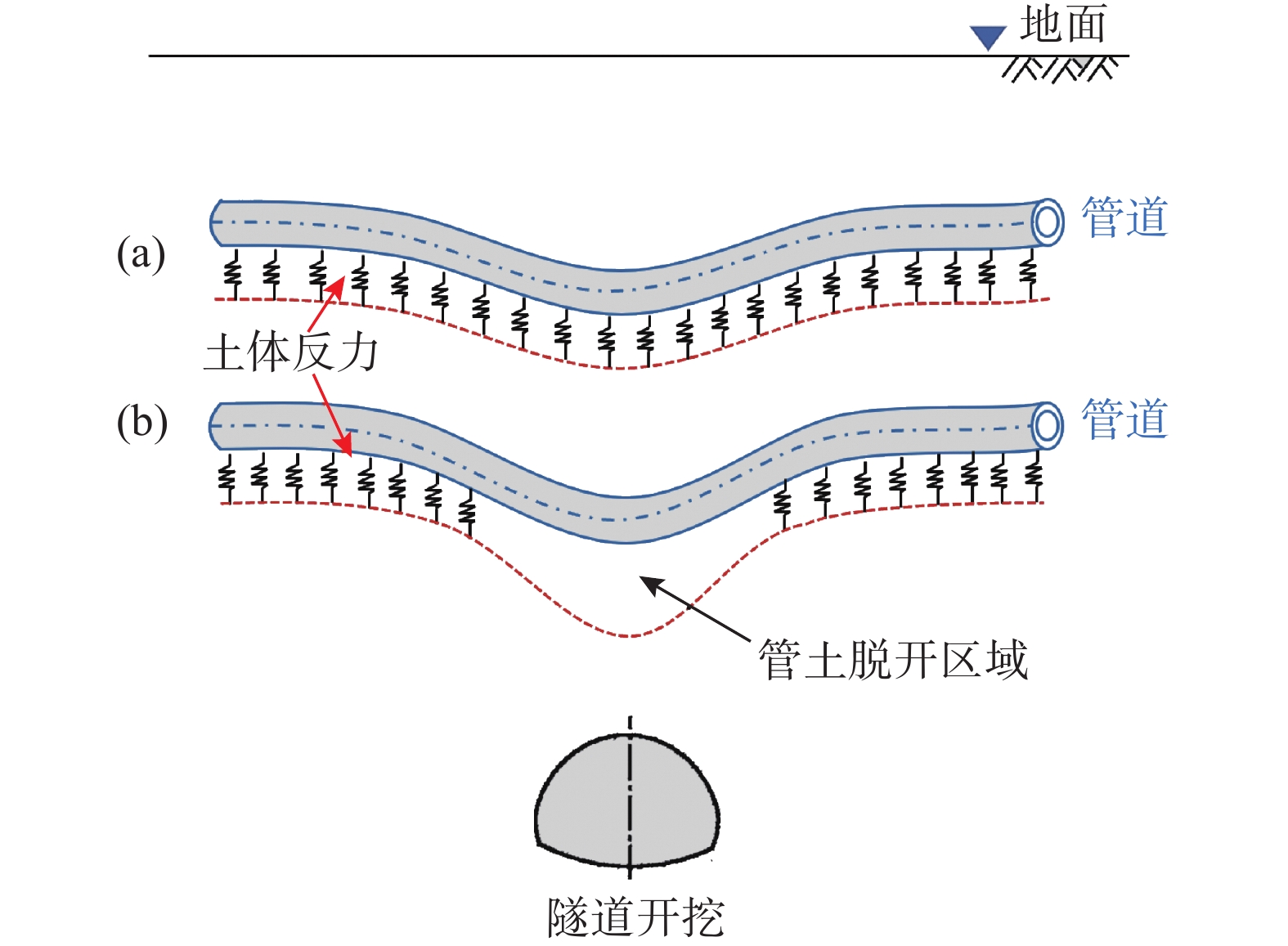
由于土体的大变形特性及管土刚度差异过大造成浅埋隧道施工时上覆管道与周围土体的脱开现象广泛存在。该文基于管道的变形分析提出浅埋隧道开挖诱发上覆管道管土脱开区的求解方法。以高斯曲线分布模拟土体变形,并基于可考虑地基连续性与非线性的Pasternak地基修正模型,分别建立浅埋隧道施工下穿管土协调区与脱开区的微分控制方程,进而利用有限差分法与牛顿迭代法得到隧道开挖诱发上覆管道竖向变形数值解,由此根据管土的位移差给出脱开区大小迭代求解步骤。提出可综合考虑管道刚度与土体强度的管土相对刚度参数R及综合考虑土体荷载特性的脱开荷载比参数Tg,将其作为管土脱开的判定参数。结合工程案例监测数据、已有模型试验数据验证了方法的正确性。管道归一化竖向位移值对比分析表明,存在临界管土相对刚度及临界且脱开荷载比参数,当R大于临界相对刚度或Tg小于临界荷载比时管土存在脱开现象,此时管道变形计算需考虑管土脱开效应。该结论可供工程设计参考。
Abstract:Due to the large deformation of soil and the large difference in the stiffness of pipe and soil, the separation of the overlying pipes and surrounding soils are widely observed during the construction of shallow buried tunnels. Proposing a method for solving the soil release zone of overlying pipeline induced by shallow buried tunnel excavation based on the analysis of pipeline deformation. The Gaussian curve distribution is used to simulate the soil deformation. Based on the nonlinear Pasternak foundation correction model, which can consider the continuity and non-linearity of the foundation, the differential governing equations of the coordination zone and the detachment zone of the pipe-soil under shallow buried tunnel construction are established, respectively. The numerical solutions of the vertical deformation of the overlying pipeline induced by tunnel excavation are obtained using the finite difference method and the Newton iteration method. According to the displacement difference of pipe-soil, the size of the release zone is solved iteratively. The relative stiffness parameter R of pipe soil, which can comprehensively consider pipe stiffness and soil strength, and detachment load ratio parameter Tg, which comprehensively considers soil load characteristics, are proposed as the judgment parameter of detachment of pipe soil. The proposed method was verified using the monitoring data of engineering cases and the existing model test data. The comparative analysis of the normalized vertical displacement of pipeline shows that there are critical relative stiffness of pipe-soil and critical and detachment load ratio parameters. When R is greater than the critical relative stiffness or Tg is less than the critical load ratio, the detachment effect of pipe-soil should be considered in the calculation of pipeline deformation. This conclusion can be used as reference for engineering design.
-
-
表 1 管道位移与土体位移计算结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of calculated pipe and soil deformation
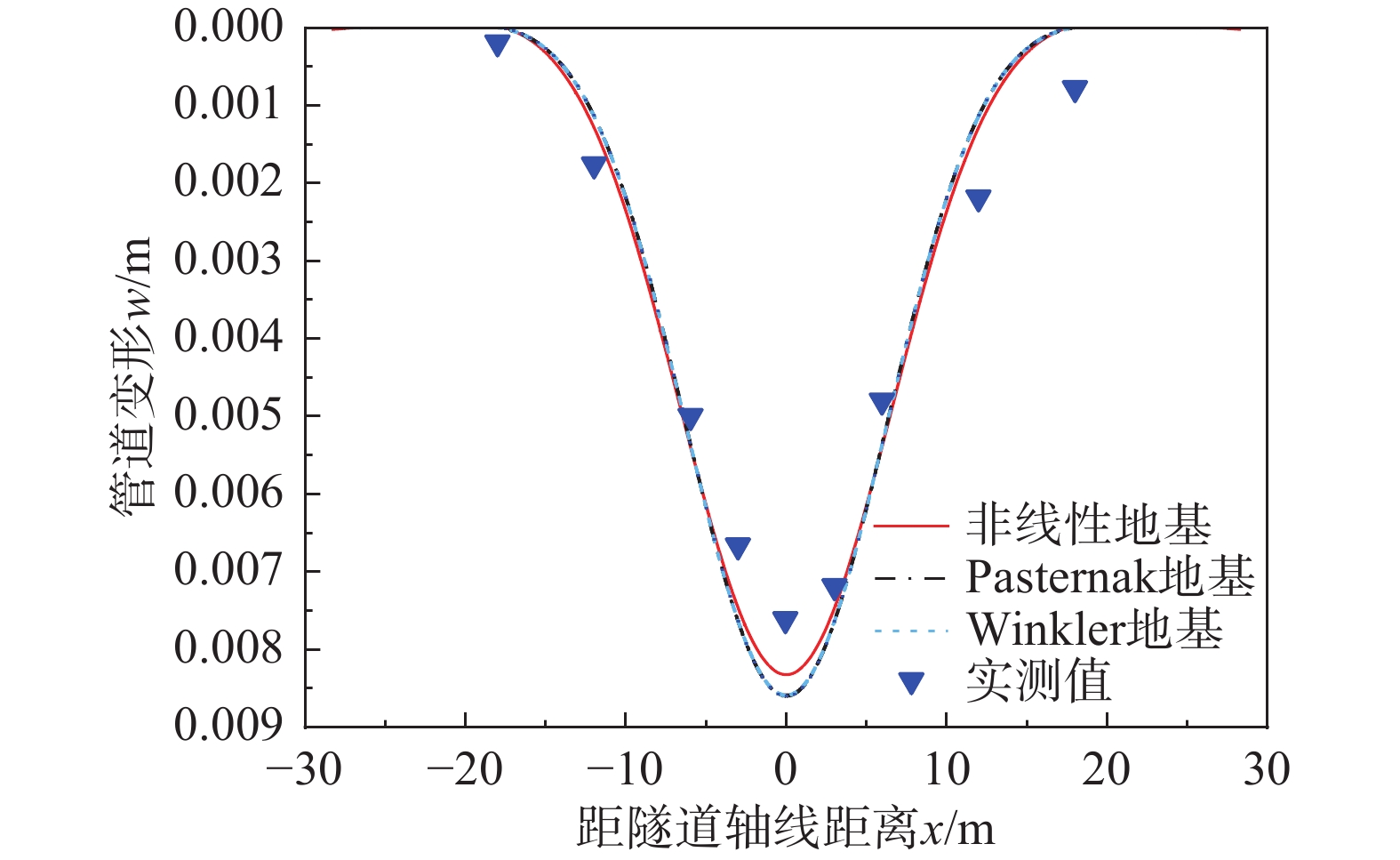
/(×10−3 m) 位移 距隧道轴线距离x 0 0.06 0.12 0.13 0.131 0.132 管道位移w(x) 0.639 0.600 0.497 0.475 0.474 0.473 土体位移S(x) 0.840 0.745 0.519 0.478 0.474 0.473 -
[1] 冯爱军. 中国城市轨道交通2021年数据统计与发展分析[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2022, 42(2): 336 − 341. FENG Aijun. Data statistics and development analysis of urban rail transit in China in 2021 [J]. Tunnel Construction, 2022, 42(2): 336 − 341. (in Chinese)
[2] 冯国辉, 徐长节, 郑茗旺, 等. 新建隧道下穿既有隧道引起的隧-土相互作用研究[J]. 工程力学, 2023, 40(5): 59 − 68. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.10.0828 FENG Guohui, XU Changjie, ZHENG Mingwang, et al. Study of tunnel-soil interaction induced by tunneling underlying [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2023, 40(5): 59 − 68. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.10.0828
[3] 马建. 盾构隧道穿越对既有管线影响的研究与展望[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2022, 59(3): 23 − 30. MA Jian. Research in the impact of shield tunnel crossing on existing pipelines and future research trends [J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2022, 59(3): 23 − 30. (in Chinese)
[4] 伊兴芳, 李鑫波. 大断面超浅埋黄土隧道长距离并行天然气管线沉降控制技术探讨[J]. 铁道建筑技术, 2015(2): 55 − 57. YI Xingfang, LI Xinbo. Analysis of settlement control technology of parallel gas pipeline along shallow buried large section loess tunnel [J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2015(2): 55 − 57. (in Chinese)
[5] ATTEWELL P B, YEATES J, SELBY A R. Soil movements induced by tunnelling and their effects on pipelines and structures [M]. Glawsgow: Blackie, Chapman and Hall, 1986: 127 − 166.
[6] KLAR A, VORSTER T E B, SOGA K, et al. Soil-pipe interaction due to tunnelling: Comparison between Winkler and elastic continuum solutions [J]. Géotechnique, 2005, 55(6): 461 − 466.
[7] 李海丽, 张陈蓉, 卢恺. 隧道开挖条件下地埋管线的非线性响应分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(增刊 1): 289 − 296. LI Haili, ZHANG Chenrong, LU Kai. Nonlinear analysis of response of buried pipelines induced by tunneling [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(Suppl 1): 289 − 296. (in Chinese)
[8] VORSTER T E, KLAR A, SOGA K, et al. Estimating the effects of tunneling on existing pipelines [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2005, 131(11): 1399 − 1410. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:11(1399)
[9] 李斌, 方宏远, 杜雪明, 等. 脱空混凝土管道纵向力学行为及自膨胀高聚物注浆修复性能提升[J]. 工程力学, $ref.ref_year. LI Bin, FANG Hongyuan, DU Xueming, et al. Longitudinal mechanical behavior of void concrete pipes and resilience improvement of self-expanding polymer grouting rehabilitation [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2005. (in Chinese)
[10] 程霖, 杨成永, 马文辉, 等. 地铁隧道开挖引起的管线变形计算与试验研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(4): 7 − 13. CHENG Lin, YANG Chengyong, MA Wenhui, et al. Deformation calculation and experimental study on buried pipes induced by subway tunnel excavation [J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(4): 7 − 13. (in Chinese)
[11] 车敬珂. 穿越施工影响下管线变形理论分析与有限差分解[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018: 20 − 30. CHE Jingke. Theoretical analysis and finite difference solution on pipeline deformation due to traversing excavation [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018: 20 − 30. (in Chinese)
[12] 杨成永, 寇鼎涛, 程霖, 等. 对称荷载作用下弹性地基梁的傅里叶级数解[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(3): 136 − 141. YANG Chengyong, KOU Dingtao, CHENG Lin, et al. Fourier series solution for elastic foundation beams under symmetric loads [J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(3): 136 − 141. (in Chinese)
[13] 许利惟, 刘旭, 陈福全. 塌陷作用下埋地悬空管道的力学响应分析[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(12): 212 − 219, 228. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.11.0837 XU Liwei, LIU Xu, CHEN Fuquan. Mechanical analysis of buried suspended pipeline under the action of collapse [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(12): 212 − 219, 228. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.11.0837
[14] 王正兴. 盾构隧道施工对既有连续管线性状影响研究[D]. 江苏: 东南大学, 2014. WANG Zhengxing. Study on mechanical behaviors of buried continuous pipelines induced by shield tunnelling construction [D]. Jiangsu: Southeast University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[15] 王正兴, 缪林昌, 王冉冉, 等. 砂土隧道施工对下卧管线影响的试验和数值模拟分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(1): 182 − 188. WANG Zhengxing, MIAO Linchang, WANG Ranran, et al. Physical model tests and PFC3D modeling of soil-pipe interaction in sands during tunneling [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(1): 182 − 188. (in Chinese)
[16] 史江伟, 范燕波, 裴伟伟, 等. 盾构下穿非连续管线变形特性及预测方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1): 143 − 150. SHI Jiangwei, FAN Yanbo, PEI Weiwei, et al. An investigation of deformation mechanisms of jointed pipelines due to underneath tunnel excavation [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 143 − 150. (in Chinese)
[17] PECK B R. Deep excavations and tunneling in soft ground [C]// Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Mexico City: ISSMGE, 1969: 225 − 290.
[18] O'REILLY M P, NEW B M. Settlements above tunnels in the United Kingdom-their magnitude and prediction [C]. London: Proceeding of Tunnelling' 82 Symposium, 1982.
[19] MAIR R J, TAYLOR R N, BRACEGIRDLE A. Subsurface settlement profiles above tunnels in clays [J]. Géotechnique, 1993, 43(2): 315 − 320.
[20] MARSHALL A M, FARRELL R, KLAR A, et al. Tunnels in sands: The effect of size, depth and volume loss on greenfield displacements [J]. Géotechnique, 2012, 62(5): 385 − 399.
[21] LIN C G, HUANG M S. Tunnelling-induced response of a jointed pipeline and its equivalence to a continuous structure [J]. Soils and Foundations, 2019, 59(4): 828 − 839. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2019.02.009
[22] Guidelines for the seismic design of oil and gas pipeline systems [S]. New York: American Society of Civil Engineers, 1984.
[23] TOHIDIFAR H, JAFARI M K, MOOSAVI M. Downwards force-displacement response of buried pipelines during dip-slip faulting in sandy soil [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2021, 58(3): 377 − 397. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2019-0446
[24] Alliance A L .Guidelines for the design of buried steel pipe [J]. Microprocessing & Microprogramming, 2005.
[25] PRCI L52292e. Guidelines for Constructing Natural Gas and Liquid Hydrocarbon Pipelines Through Areas Prone To Landslide and Subsidence Hazards [S]. 2009.01.30
[26] 林存刚, 黄茂松. 基于Pasternak地基的盾构隧道开挖非连续地下管线的挠曲[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(7): 1200 − 1207. LIN Cungang, HUANG Maosong. Deflections of discontinuous buried pipelines induced by shield tunnelling based on Pasternak foundation [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(7): 1200 − 1207. (in Chinese)
[27] SELVADURAI A P S, GLADWELL G M L. Elastic analysis of soil-foundation interaction [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1980, 47(1): 219.
[28] LIN C C, HUANG M S, NADIM F, et al. Tunnelling-induced response of buried pipelines and their effects on ground settlements [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 96: 103193. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.103193
[29] 王磊, 李家宝. 结构分析的有限差分法[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1982: 4 − 11. WANG Lei, LI Jiabao. Finite difference method of structural analysis [M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 1982: 4 − 11. (in Chinese)
[30] 程霖. 地铁隧道开挖引起地下管线变形的理论分析和试验研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021. CHENG Lin. Theoretical analysis and experimental research on deformation of buried pipelines due to subway tunnel excavation [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[31] MA S K, SHAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Responses of pipeline to side-by-side twin tunnelling at different depths: 3D centrifuge tests and numerical modelling [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 66: 157 − 173. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.04.006



 下载:
下载: