EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON SEISMIC AND REPLACEABLE PERFORMANCE OF REPLACEABLE ENERGY DISSIPATION BEAMS WITH BOLTED END PLATES
-
摘要: 为研究端板-螺栓连接可更换耗能梁的抗震及可更换性能,设计制作了4个可更换耗能梁试件并进行了拟静力试验,研究不同长度系数对可更换耗能梁抗震性能和可更换能力的影响。结果表明:当长度系数较小时,试件发生剪切破坏,破坏特征包括腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂、腹板屈曲和腹板撕裂;当长度系数较大时,试件发生弯剪破坏,破坏特征包括梁端翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂和梁端翼缘屈曲;所有试件的滞回曲线非常饱满,具有优异的变形能力和耗能能力;可更换耗能梁的抗剪承载力强化明显,超强系数均值为1.9;采用端板-螺栓连接的可更换耗能梁均可实现震后可更换,当梁端残余转角为0.0020 rad~0.0046 rad时耗能梁可以实现震后更换,且更换快捷、操作简单;同时,根据耗能梁构件与带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构体系的几何变形特征,可以将耗能梁的主要受力阶段划分为正常使用、非必要更换和必要更换3个阶段。Abstract: To study the seismic performance and replaceable capacity of energy dissipation beams with bolted end plates, four replaceable energy dissipation beam specimens were designed and fabricated. The effects of length ratio on seismic performance and replaceable capacity of the replaceable energy dissipation beams were investigated through quasi-static test. The results show that specimens with small length ratio present a shear dominated behavior including web-to-stiffener weld fracture, web buckling and web tear. Whereas the failure features of shear and flexure dominate the behavior of specimens with large length ratio, manifested as flange buckling and end plate-to-flange weld fracture. All tested specimens exhibit stable hysteresis behavior, excellent deformation ability and energy dissipation capacity. In addition, the bearing capacity of replaceable energy dissipation beams is strengthened significantly, and the average value of the overstrength factor is about 1.9. The replaceable energy dissipation beams with bolted end plates can be replaced after the earthquake. Moreover, the energy dissipation beams can be replaced conveniently after the earthquake when the residual angle at the beam end is 0.0020 rad-0.0046 rad. Meanwhile, the main stress development of replaceable beams can be divided into three stages of serviceability, non-essential and mandatory replaceability according to the deformation relationship between the replaceable link beams and the proposed frame structure system.
-
工程结构抗震设防的首要目标是防止大震作用下结构倒塌、避免人员伤亡。多次震害表明,按照现行抗震规范[1]设计的建筑能够实现“小震不坏、中震可修、大震不倒”的设计目标。然而,建筑结构的主要构件在地震损坏后修复成本高,甚至需拆除重建,从而导致巨大经济损失和影响建筑的正常使用功能,因此希望地震中建筑不发生损坏或者损坏后建筑使用功能可快速恢复。针对传统建筑震后修复能力不足的问题,工程结构的抗震设计理念逐渐从防倒塌转向可维持、可恢复[2]。
目前,可恢复功能结构体系的研究主要集中在可更换结构[2]、摇摆结构[3]和自复位结构[4]。其中,可更换结构因为其力学概念明确、施工方法简单、震后可恢复能力强等优势而逐渐得到了广泛重视[2]。姜子钦等[5]针对装配式钢框架结构设计了一种可更换抗侧耗能装置,结果表明,结构的塑性损伤能够集中在翼缘连接盖板与抗侧耗能装置等易于更换的耗能元件上,而梁柱等主体构件基本处于弹性状态,具备震后可恢复功能。张浩等[6-8]针对钢框筒结构提出可更换剪切型耗能梁段,试验研究表明,结构的损伤集中在耗能梁段,框筒柱和裙梁处于弹性状态,有利于震后的快速修复。纪晓东等[9-10]针对剪力墙结构设计了由跨中消能梁段和两端非消能梁段组成的可更换连梁,进行了拟静力试验,结果表明,结构的塑性变形和损伤能够集中在跨中消能梁段,具有稳定的滞回耗能能力,且震后易于更换。MANSOUR等[11]针对偏心支撑框架结构设计了一种可更换连系梁段,结果表明连系梁具有良好的耗能能力且不同形式连接的耗能结果与文献[12]一致。
目前,对可更换结构的研究大多集中在联肢剪力墙结构体系[13]和偏心支撑框架结构[14]。为了能在框架结构中实现可恢复功能,谢鲁齐等[15]在装配式混凝土框架梁端上、下纵向钢筋位置设计并安装可更换耗能连接件,震后损伤集中在可更换耗能连接件,增强结构的可修复性;孙东德等[16]在梁柱连接处设置可更换钢连接件,震后通过更换钢连接件和连接角钢可实现抗震性能的恢复;黄炜和胡高兴[17]针对预制装配式RC梁柱节点提出一种可恢复梁柱节点连接形式,研究表明该连接形式抗震性能优于现浇,同时可以实现节点损伤位置可控便于震后快速修复;叶建峰等[18]提出一种装配式可更换耗能铰,震后更换耗能铰中的金属阻尼器前后抗震性能指标基本一致。
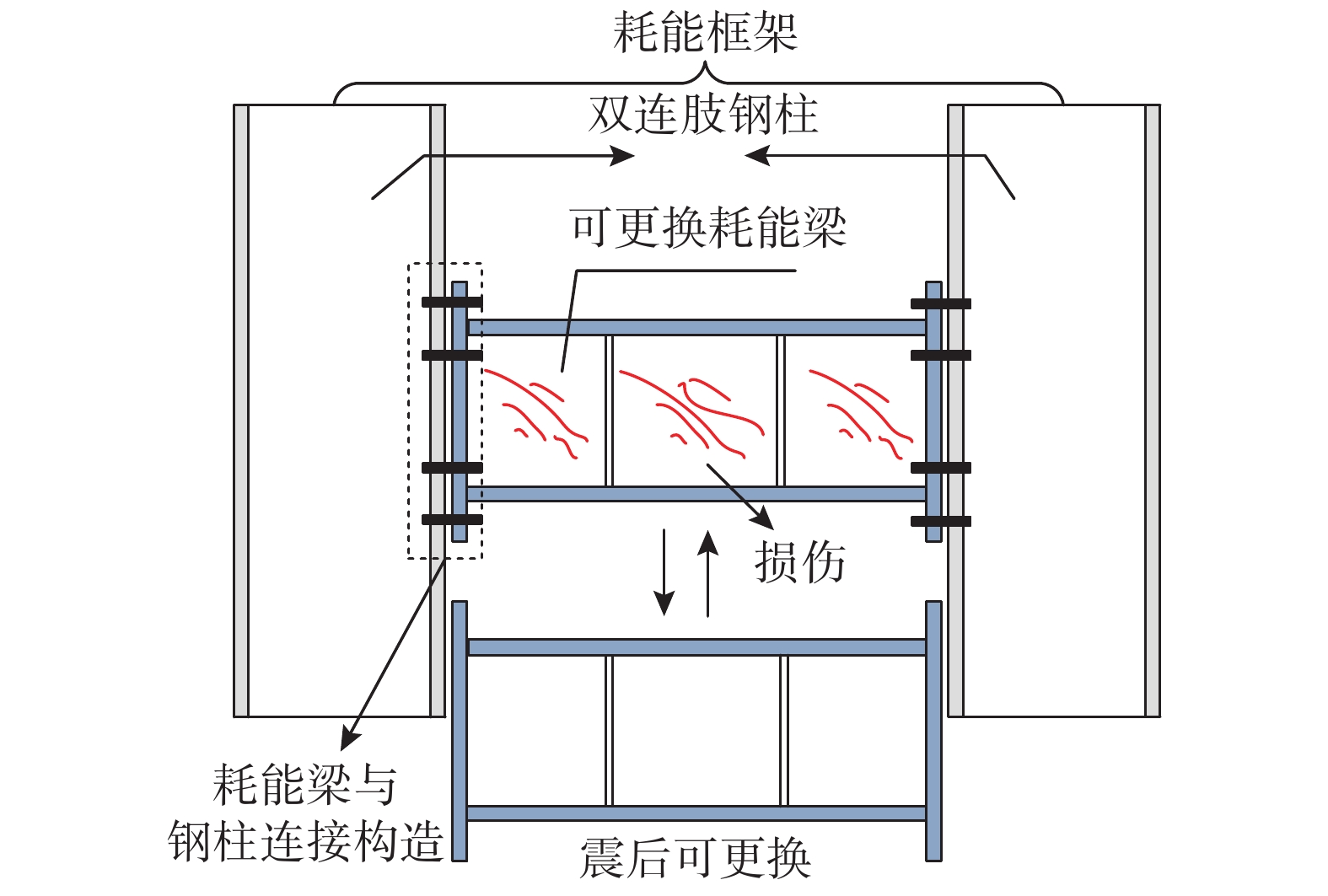
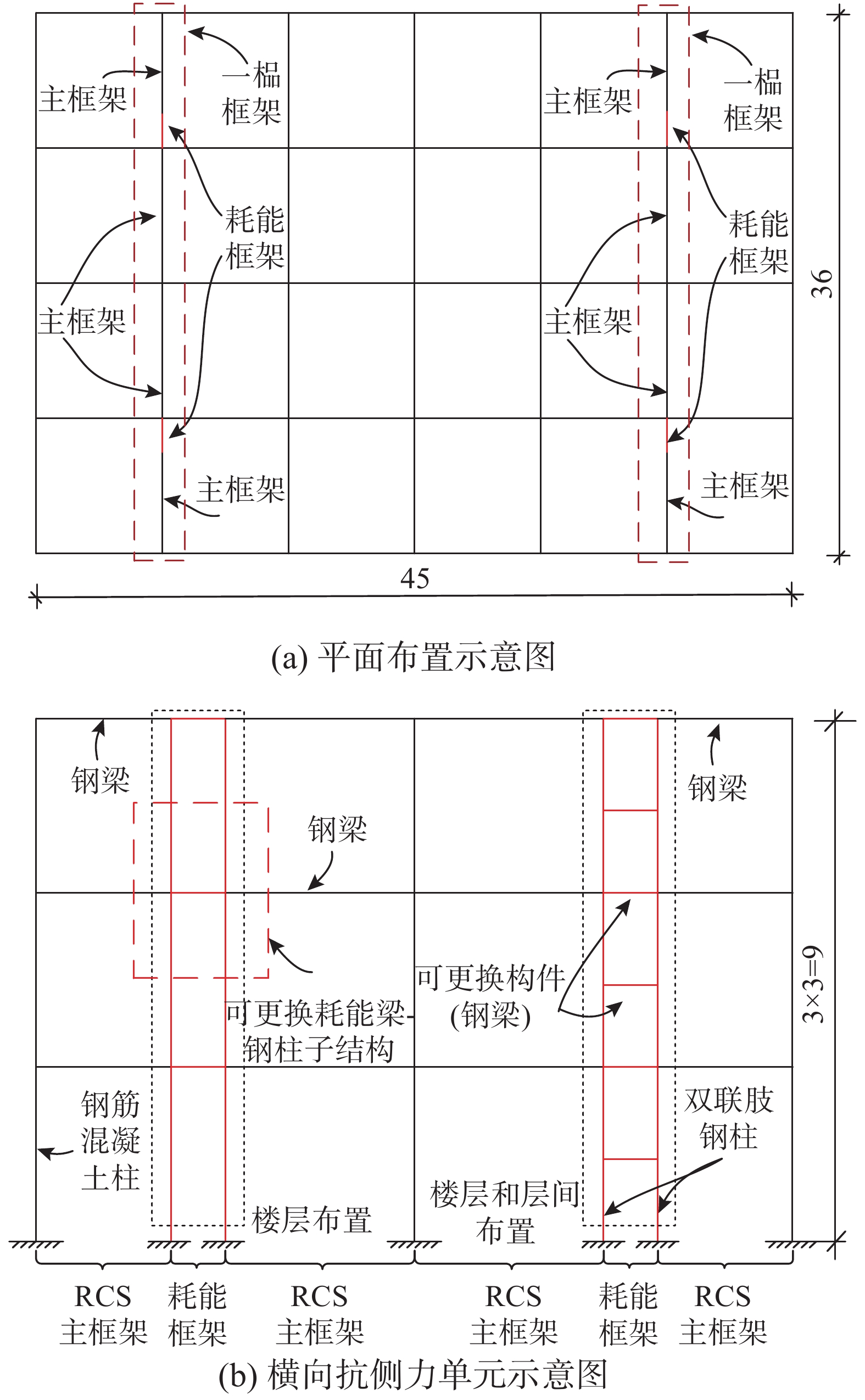
以上研究均表明在框架结构梁柱节点处设置可更换耗能构件能够实现损伤集中,并提高结构的可恢复性能,但梁柱节点处耗能能力有限,且在结构中分布较广,无法快速确定受损节点位置并进行修复。为了提高RCS组合框架结构震后功能的可恢复性,本课题组在RCS组合框架中引入一带可更换构件的耗能框架,提出一种带可更换构件的钢筋混凝土柱-钢梁(RCS)混合框架结构体系,该结构体系由RCS主框架和耗能框架构成,耗能框架是由可更换钢梁和双联肢钢柱组成的连肢钢框架。图1为其平面布置图和横向抗侧力单元示意图。其中,可更换构件与钢柱采用可拆卸连接构造,根据需求可以采用仅在楼层布置或楼层与层间均布置的形式。
研究表明[19],该结构体系具有“3个受力阶段、5个性能水准”的预期受力特征,其中耗能框架中的可更换钢梁首先集中耗散能量,因此应当首先满足抗震耗能特征,并在此基础上实现其震后可拆卸与可更换,满足其可更换性能,以达到恢复RCS混合框架结构体系预定功能的目的。为研究可更换耗能梁的抗震及可更换性能,本文共设计了4个整段式可更换耗能梁试件,以不同长度系数为研究对象,通过低周往复加载试验,研究试件的破坏特征、耗能能力、承载能力和变形能力等抗震性能指标。最后对可更换耗能梁试件的可更换性进行了分析,以及整体混合框架结构中试件的可更换性能分析,得出可更换耗能梁根据主要受力阶段可以分为正常使用、非必要更换和必要更换阶段。
1 试验概况
以一幢3层带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构体系为工程背景[20],建筑平面为45 m×36 m,结构总高度9 m。如图1(b)所示,从结构第2层和第3层柱的反弯点处选取楼层布置形式的可更换耗能梁-双连肢钢柱子结构进行试验。
1.1 试件设计
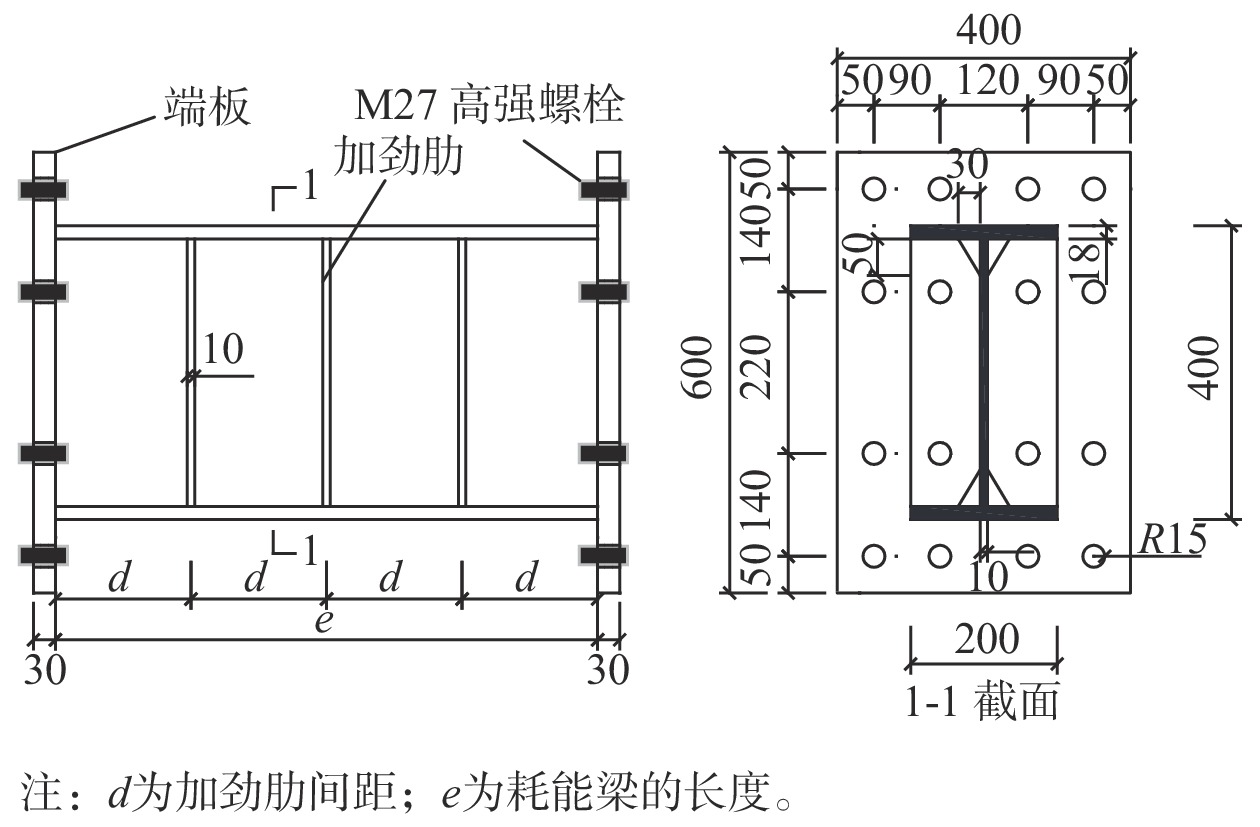
如图2所示,试件采用组合截面,尺寸为I400 mm×200 mm×10 mm×18 mm。试件翼缘宽厚比(bf/2tf)为5.5,腹板高厚度比(h0/tw)为36.4,均满足规范GB 50011−2010[1]和AISC 341-10[21]关于耗能梁段宽厚比与高厚比限值规定。试件翼缘采用Q345级钢,腹板采用Q235级钢。双连肢钢柱的截面尺寸为I600 mm×400 mm×18 mm×25 mm,材料选用Q345级钢。表1给了相应构件各部分的厚度t、屈服强度fy、抗拉强度fu、弹性模量E以及断后伸长率δ等性能指标。
表 1 材料性能Table 1. Material properties钢材类型 部位 厚度t/mm 屈服强度fy/MPa 抗拉强度fu/MPa 强屈比fu/fy 屈服应变εy/με 弹性模量E/(×105MPa) 延伸率δ/(%) Q235 耗能梁腹板 10 291.7 441.7 1.51 1383 2.11 41.5 Q345 耗能梁翼缘和钢柱腹板 18 391.7 538.3 1.37 1967 1.99 42.5 Q345 钢柱翼缘 25 443.2 554.5 1.25 2161 2.07 42.7 1.1.1 试件长度系数
长度系数是影响试件破坏类型的关键参数之一。当耗能梁的长度系数e/(Mp/Vp)<1.6时,试件发生剪切型破坏;试件的长度系数介于1.6~2.6时,试件发生弯剪型破坏;试件的长度系数大于2.6时,试件发生弯曲型破坏。研究表明当耗能梁发生剪切型破坏,试件的塑性变形能力与耗能能力较其他破坏形式更优越[21-24]。本文设计的耗能梁长度系数介于0.68~1.60,属于剪切型耗能梁。即试件承载力满足式(1)~式(3):
e/(Mp/Vp)⩽ (1) {M_{\text{p}}} = {f_{\text{y}}}Z (2) {V_{\text{p}}} = 0.58{f_{\text{y}}}{A_{\text{w}}} (3) 式中:e为耗能梁的长度;Mp、Vp分别为耗能梁段的全截面屈服弯矩和屈服剪力;fy为钢材的屈服强度;Z为耗能梁的塑性截面模量;Aw为耗能梁腹板的面积。
1.1.2 试件构造措施设计
各试件采用双面加劲肋,加劲肋厚度为max{0.75tw,10 mm},取值为10 mm,间距满足小于(30tw − h/5)限值的要求。梁端端板厚度为30 mm,宽度与柱翼缘宽度保持一致,端板尺寸600 mm×400 mm×30 mm,采用Q235钢,螺栓选用10.9级公称直径为27 mm的高强摩擦型螺栓,试件连接处钢板接触面进行喷丸处理,抗滑移系数取0.45。试件的翼缘、腹板和端板之间均采用全熔透对接焊缝连接。加劲肋与腹板、加劲肋与翼缘之间采用双面角焊缝连接,焊脚高度为8 mm,并对加劲肋角部进行部分切割,切割高度为5倍腹板厚度,目的是减小翼缘与腹板焊接区域的应力集中现象以及避免往复荷载作用下翼缘、腹板和加劲肋交汇处焊接热影响区过早开裂[24]。试验试件具体参数和构造如表2所示。
表 2 试件参数Table 2. Specimen parameters试件
编号截面形式/
(mm×mm×mm×mm)耗能梁
长度e/mm长度系数
e/(Mp/Vp)加劲肋布置 试件
梁端构造间距d/mm 布置
形式RB1 I400×200×10×18 740 0.68 4@185 双侧 端板螺栓
连接RB2 940 0.86 5@188 RB3 1140 1.05 6@190 RB4 1740 1.60 8@218 1.2 试验装置与加载制度
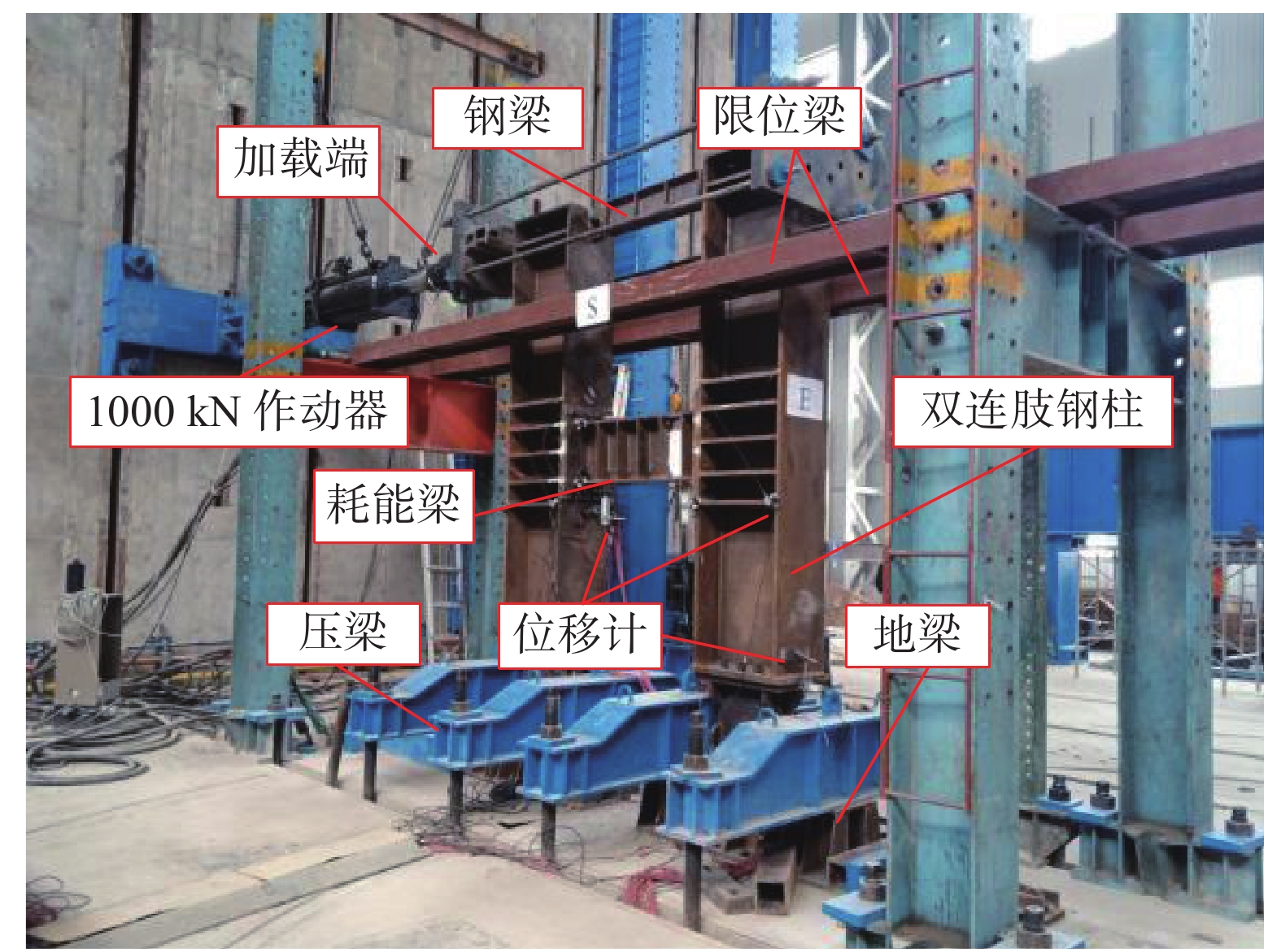
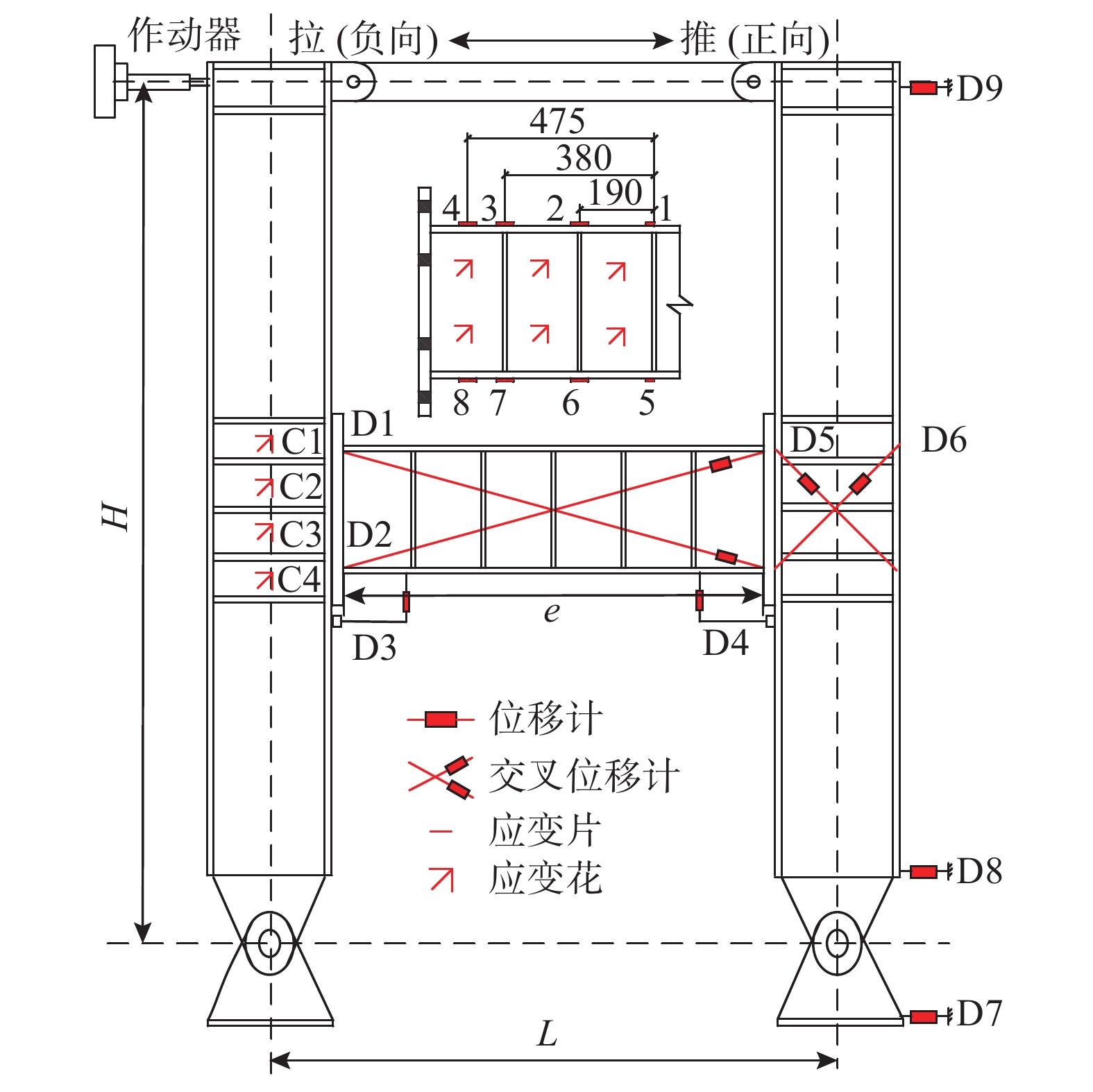
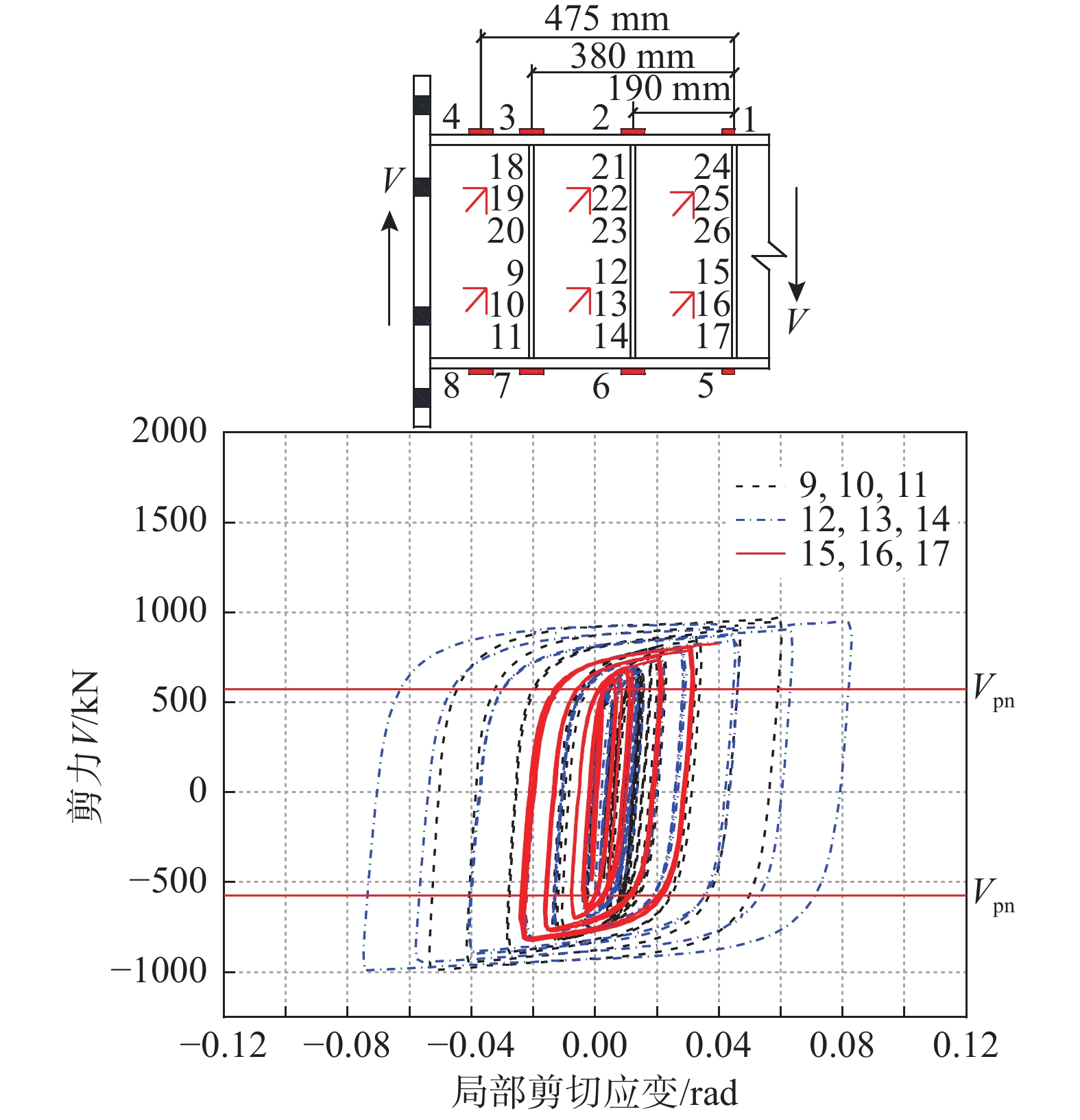
本次试验采用柱端往复加载方式,试验加载装置设置如图3所示。钢柱柱顶通过轴向杆件铰接连接,钢柱柱底与地梁采用铰接,钢柱上部两侧设置限位梁,限制试件平面外失稳。电液伺服作动器在左侧钢柱顶端施加往复水平位移,以作动器施加推力为正向加载,施加拉力为负向加载。变形测量的主要内容包括子结构的整体侧向位移、耗能梁的剪切位移和梁-柱节点区的剪切变形;应变测量包括耗能梁腹板和翼缘的应变以及钢柱节点区应变等,如图4所示。
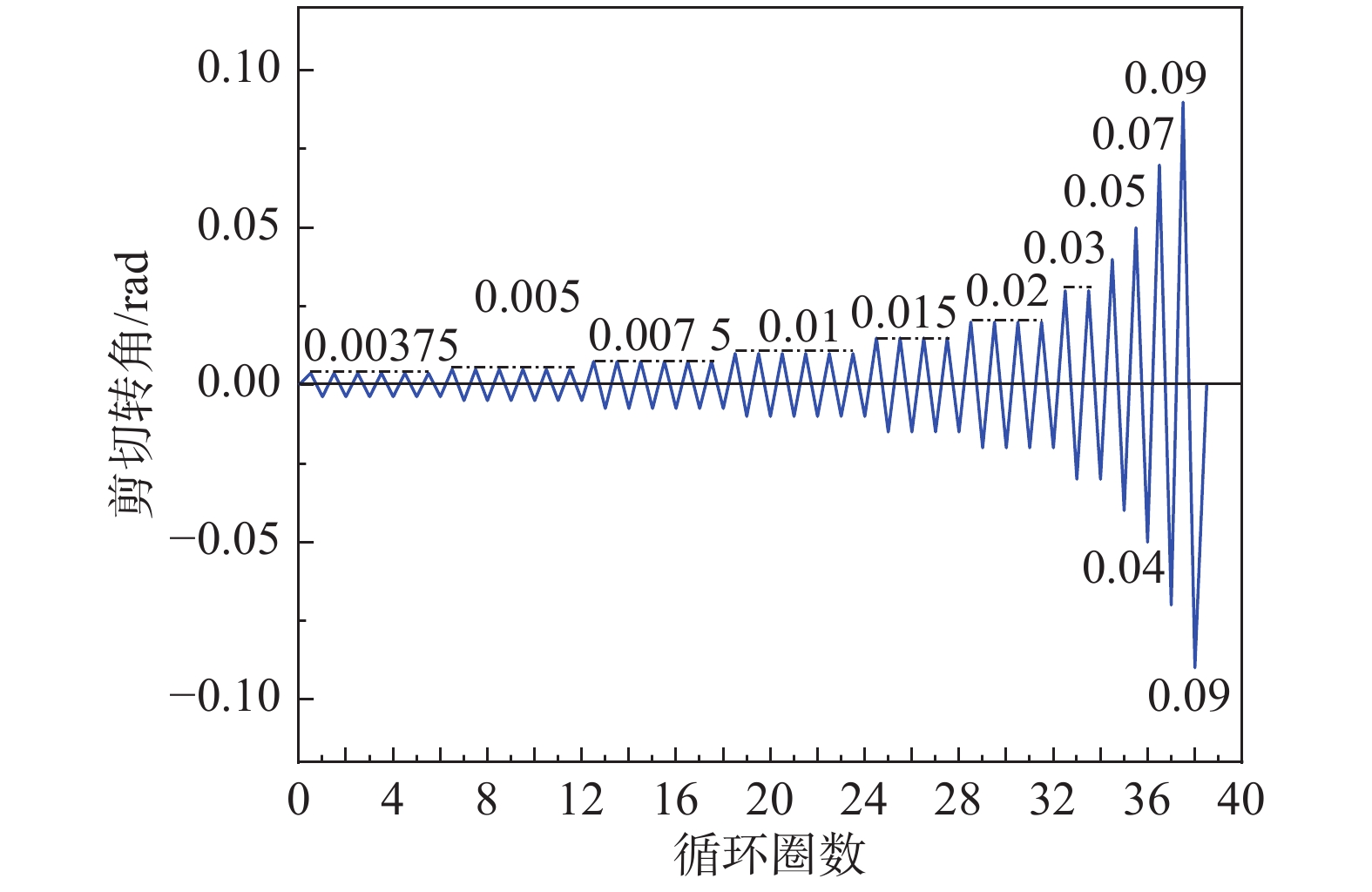
试件的加载制度如图5所示。采用RICHARDS和UANG[25]在AISC(2002)基础上,提出的一种适用于耗能构件的位移加载制度,该加载制度能够更好地反映地震作用下试件的受力性能。
2 可更换耗能梁抗震性能分析
2.1 试件的破坏过程与破坏特征
图6为4个试件的整体破坏图,在加载过程中,试件主要呈现出5种典型受损特征,分别为腹板-加劲肋焊缝断裂、腹板鼓曲、腹板撕裂、梁端翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂和梁端翼缘屈曲,如图7所示。试件裂缝首先出现在腹板与加劲肋焊缝端部或者翼缘与端板焊缝处的钢材热影响区,然后逐渐扩展,腹板裂缝沿加劲肋角部向腹板中部斜向发展,而钢梁翼缘与端板焊缝呈掰开撕裂状。腹板撕裂或者翼缘端部断裂,导致试件承载力下降,最终破坏。
对于长度系数较小的试件RB1~RB3发生的是剪切屈服型破坏,主要破坏特征包括腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂、腹板鼓曲和腹板撕裂。在0.005 rad~0.01 rad时,试件RB1~RB3腹板相继屈服,且随着试件长度系数的增大,试件的腹板屈服位移增大;在0.02 rad时,试件RB1~RB3出现翼缘屈服;在0.05 rad时,试件RB1和RB2出现腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂,试件RB3无明显变化;在0.07 rad时,试件RB1和RB2出现腹板屈曲,试件RB3出现腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂;在0.09 rad时,试件RB1腹板出现沿加劲肋角部向腹板中部斜向发展的撕裂焊缝,试件RB2和RB3腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂进一步加深,但撕裂程度相对减弱,除此之外,各试件腹板严重屈曲。随着长度系数的增加,同类型损伤特征加载位移延后,其主要原因是试件由剪切变形向弯剪变形转变。
对于长度系数较大的试件RB4发生的是弯剪屈服型破坏,主要特征包括梁端翼缘-端板焊缝断裂和梁端翼缘屈曲。这种破坏模式与MCDANIEL等[24]、OKAZAKI和ENGELHARDT[26]等学者试验中耗能梁的破坏特征相似。在0.01 rad时,试件RB4腹板进入屈服;在0.015 rad时腹板出现轻微屈曲现象;在0.02 rad时出现翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂现象,其主要原因为梁端翼缘与端板焊缝在往复拉、压和局部弯曲作用下应力集中,焊缝区域产生撕裂破坏。在0.05 rad时出现梁端翼缘屈曲,与此同时翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂程度加深;在0.07 rad时翼缘焊缝撕裂过大,试件破坏,加载结束。
2.2 滞回性能
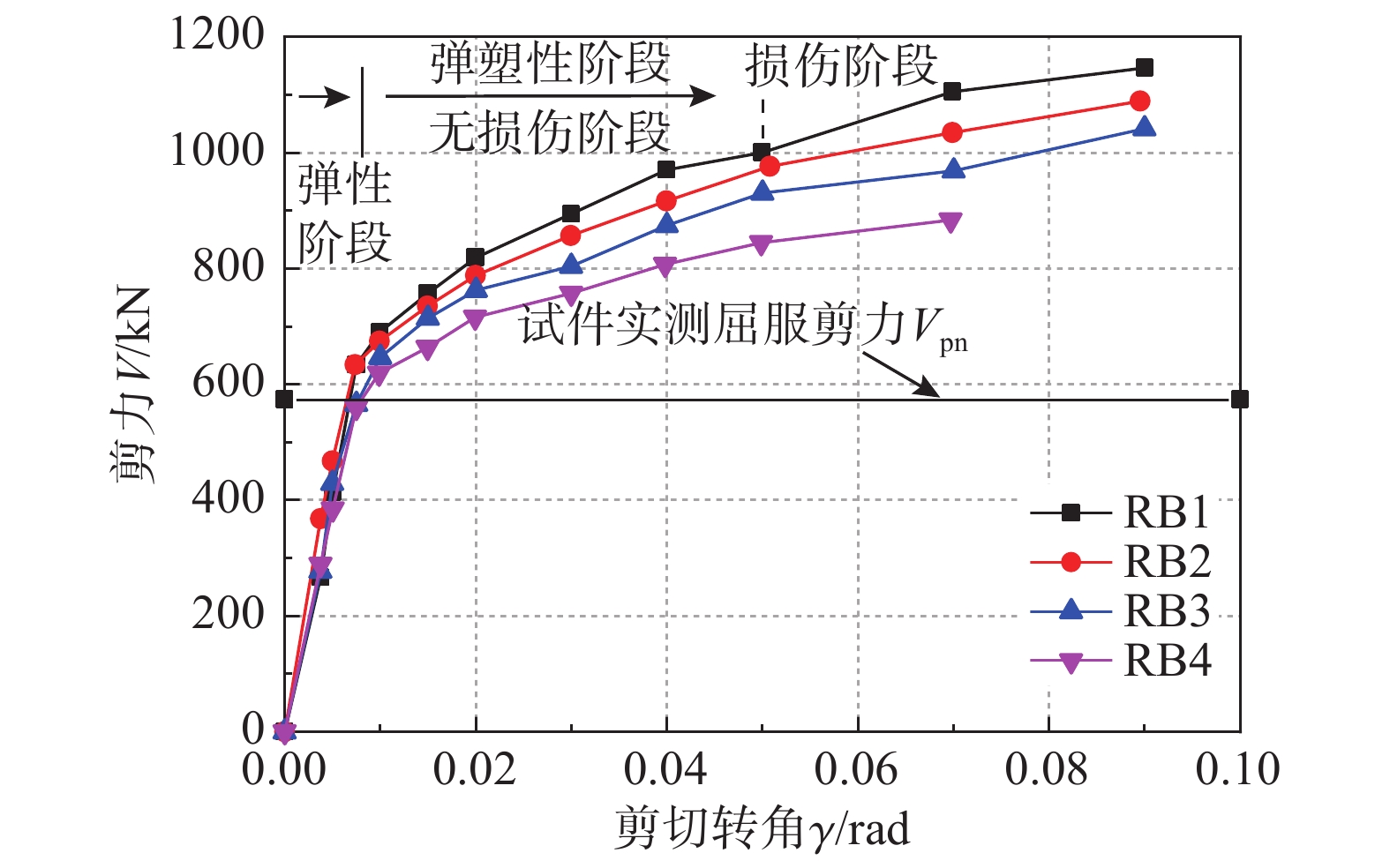
耗能梁本身是耗能构件,在实现震后可更换功能的同时,还应具备良好的耗能能力。图8所示为试件的剪力-塑性转角滞回曲线。剪力用试件剪切荷载表征,塑性转角为试件实测极限转角减去其弹性转角,弹性转角由试件屈服剪力除以试件实测刚度得到。图中还给出了各试件的实测屈服剪力值Vpn和名义屈服剪力值Vp。计算实测值时采用钢材的实测屈服强度和实测截面面积,计算名义值时采用钢材的名义屈服强度和名义截面面积。试件腹板采用Q235钢,其屈服强度实测值大于其名义值,各试件的Vpn值比Vp值大15%左右。
由图8可知,试件RB1~RB3的滞回曲线非常饱满,具有优异的变形能力和耗能能力,相比之下试件RB4的承载力、变形和耗能能力较弱。在加载初期,各试件基本保持弹性状态,滞回曲线呈狭窄细长型,包围面积较小,卸载后试件的残余应变很小;屈服后,滞回环面积不断增大,卸载时也出现较大的残余变形;达到峰值荷载后,试件仍具有很强的承载能力和耗能能力。随着试件长度系数的增大,试件滞回曲线饱满程度减弱,滞回曲线包围面积减小。
2.3 骨架曲线
图9所示为试件的剪力-剪切转角骨架曲线。在整个加载过程中,试件抗剪承载力随加载位移的增加而增大,直到试件破坏,试件承载力依然缓慢增加;试件经历了弹性阶段和弹塑性阶段,其中弹塑性阶段包括无损伤阶段和损伤阶段。由图9可知,对于剪切型试件,屈服后刚度相应的约降低到28%,且随着长度系数的增大,试件的抗剪承载力降低,试件RB3较RB1抗剪承载力降低约5%;当试件发生弯剪破坏时,试件RB4变形能力减弱约22%,抗剪承载力较剪切型试件RB1降低约33%。
2.4 承载力及超强系数
试件极限抗剪承载力与实测屈服剪力比值为试件的超强系数。表3所示为试件的抗剪承载力和超强系数。可以看出,随着长度系数的增加,试件的超强系数下降。其主要原因为在加载过程中试件腹板钢材的应力强化效应以及型钢翼缘对抗剪能力的贡献。
表 3 试件抗剪承载力和超强系数Table 3. Shear capacity and overstrength of specimens试件
编号实测屈曲
剪力Vpn/kN极限抗剪
承载力Vu/kN超强
系数ΩRB1 573.3 1190.1 2.07 RB2 573.3 1133.4 1.98 RB3 573.3 1131.0 1.97 RB4 573.3 894.5 1.56 当发生剪切破坏时,破坏模式为腹板撕裂,在加载过程中钢翼缘未发生屈曲或破坏,因此钢翼缘能够充分发挥其抗剪承载力[27],且RB1~RB3试件产生的塑性转角大,钢腹板的应力强化程度高,因此提高了抗剪承载力,3个试件的超强系数均值为2.0;发生弯剪破坏时,破坏模式为钢翼缘屈曲并且翼缘与端板焊缝撕裂,这便导致钢翼缘的抗剪承载力降低,因此文中剪切型试件的超强系数大,弯剪型试件超强系数小,试件RB4的超强系数值为1.56。
对于长度系数e小于1.0的剪切型耗能梁,超强系数接近2.0,比规范AISC 341-10[21]建议值提高了33.3%,在实践工程中试件的超强系数若仍按采用1.5设计显然不合理,通过本文试验,对于发生剪切型破坏的试件超强系数建议取各试件的超强系数平均值为1.9。
2.5 试件变形能力与耗能能力
2.5.1 变形能力
试件的塑性转动能力是评价试件耗能能力大小的关键参数。试件的塑性转角如表4所示。
表 4 试件变形能力Table 4. Deformation capacity of specimens试件
编号屈服转角
γy/rad极限塑性
转角γp/rad累积塑性转角
Σγp/rad累积延性
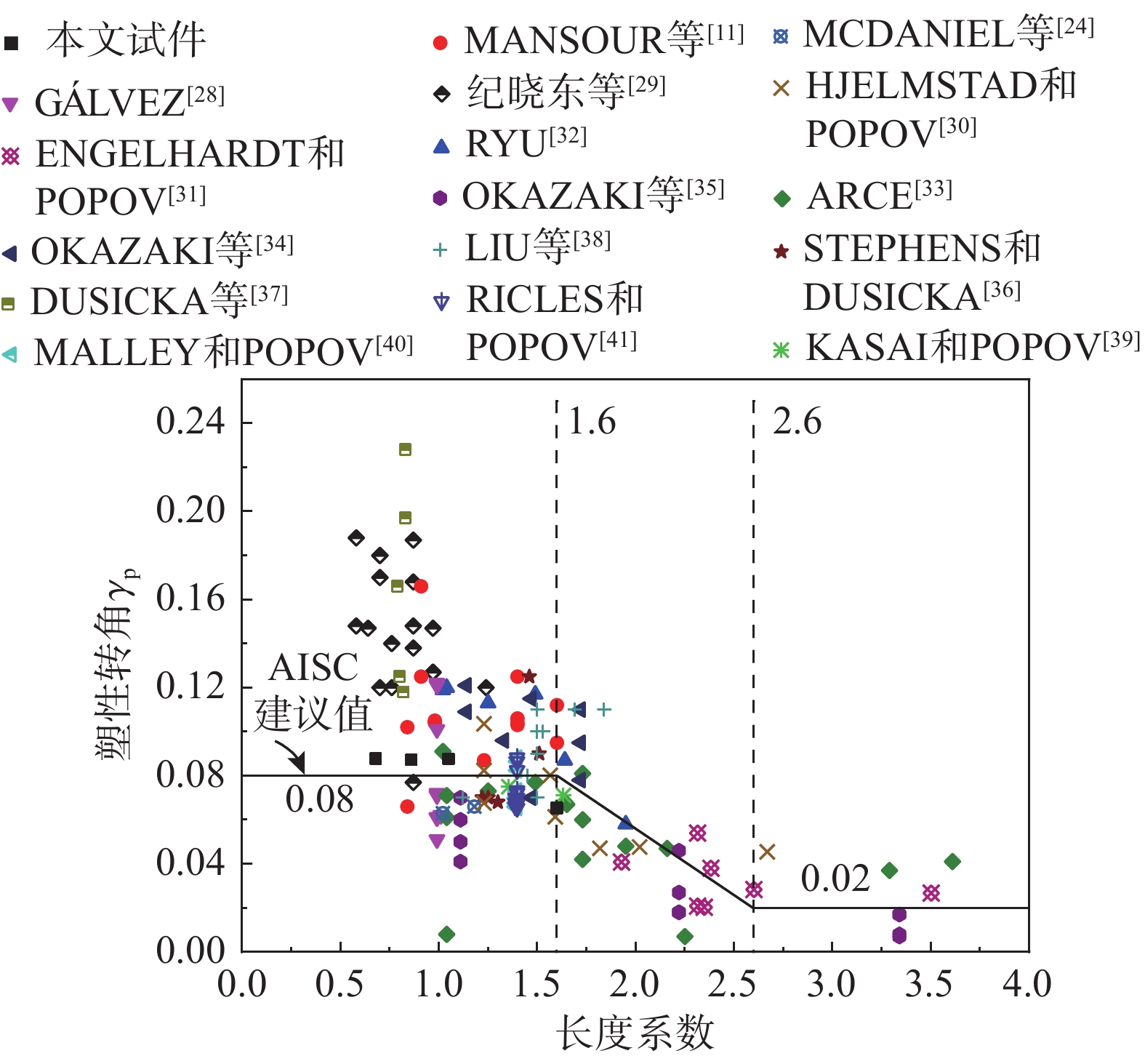
系数Σγp/γyRB1 0.00225 0.0877 1.26 560 RB2 0.00292 0.0871 1.38 473 RB3 0.00234 0.0876 1.32 564 RB4 0.00467 0.0652 0.97 208 美国ANSI/AISC 341-10中对偏心支撑钢框架耗能梁的塑性转角作了相应规定[21],长度系数小于等于1.6时,塑性转角γp为0.08 rad;长度系数大于等于2.6时,塑性转角γp为0.02 rad,其他长度系数值按线性插入法计算。由表4可知,试件RB4的极限剪切塑性转角比0.08 rad略小,其他试件均比0.08 rad略大。这是由于试件RB4发生了弯剪破坏,梁端翼缘过早出现屈曲,试件极限塑性转角略小。
图10为本文试件与国内外学者所研究的剪力墙连梁或偏心支撑框架耗能梁段[11, 24, 28-41]的塑性转角与长度系数结果对比。由图可知,本文4个耗能梁的塑性转动能力整体趋势与美国ANSI/AISC 341-10[21]规定限值相吻合,因此对于剪切型耗能梁,试件梁端采用可拆卸连接构造时,试件的变形能力可以采用塑性转角0.08 rad的限值进行评价。
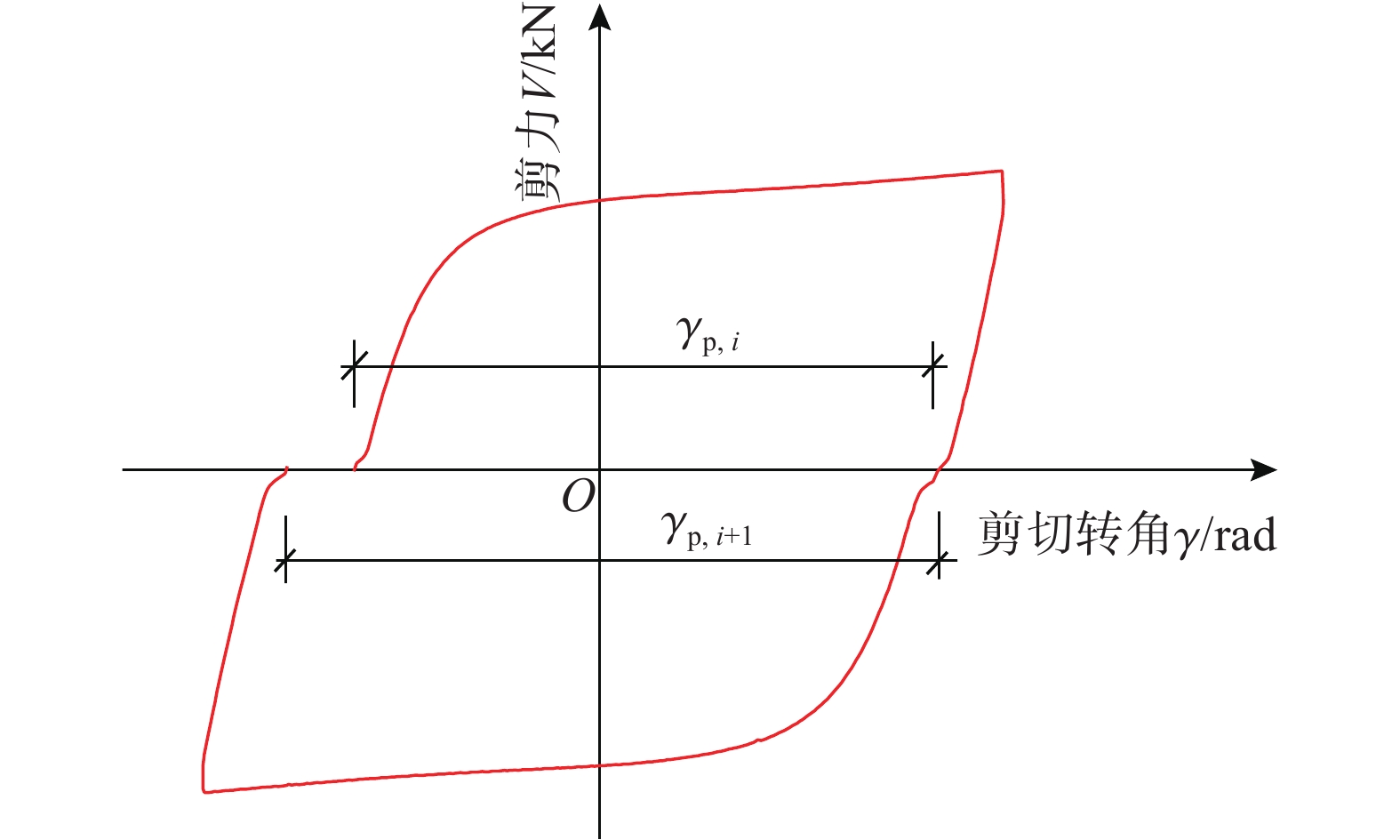
表4中还给出了试件的累积塑性转角和累积延性系数。试件在地震作用下,由于加速度的累积循环效应导致试件出现累积损伤破坏,可采用累积塑性转角评价其损伤。如图11所示,试件的累积塑性转角Σγp由每个半圈加载的塑性转角绝对值累加得到,按式(4)计算,即:
\sum {{\gamma _{\text{p}}}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left| {{\gamma _{{\text{p}},i}} + {\gamma _{{\text{p}},i + 1}}} \right|} (4) 式中:γp,i、γp,i+1分别为节点第i、i+1次循环卸载为零时的残余转角;n为水平荷载下降至峰值荷载85%或者试件破坏时前一个循环的总循环次数。
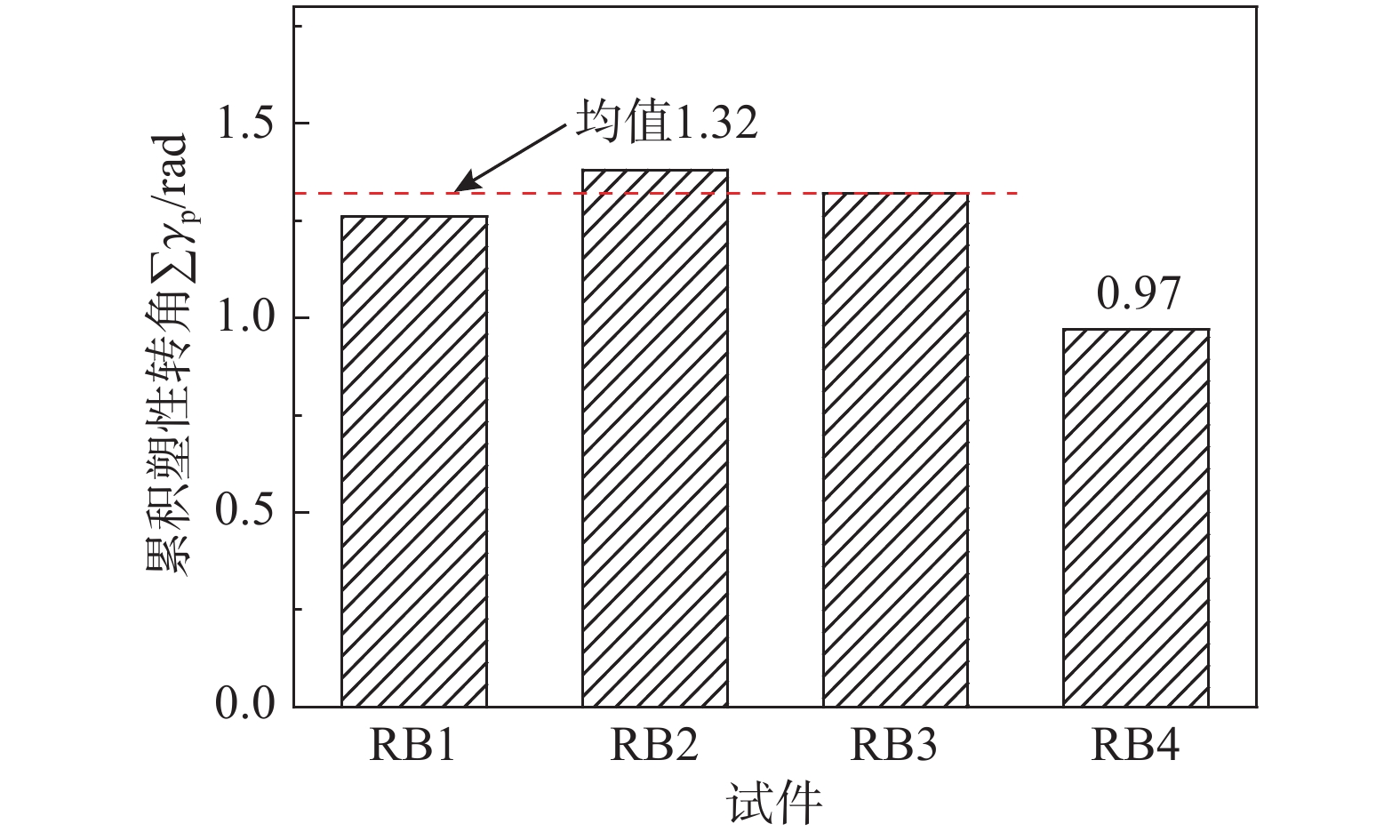
图12为试验试件的累积塑性转角,由图可知,随着试件的长度系数增大,剪切型耗能梁的累积塑性转角变化较小,均值为1.32 rad,比弯剪型试件RB4提高了约36%,其主要原因为试件的破坏模式不同。
2.5.2 耗能能力
对抗震设防结构体系进行设计时,结构在循环荷载作用下每个运动周期的能量耗散量决定了结构的有效阻尼系数。带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构体系中耗能梁试件发生剪切屈服耗能,为了较好地评价耗能梁滞回耗能能力,引入能量耗散归一化系数Eh,norm进行描述,计算方法如图13所示。
图13为各试件的能量耗散系数。由图可知,当试件剪切变形小于0.01 rad时,试件的能力耗散系数对位移呈线性变化;当试件剪切变形大于0.02 rad时,即试件处于明显塑性耗能阶段,试件的能力耗散系数依然缓慢增加,试件呈现出良好的耗能能力。随着长度系数的增加,剪切型试件的能力耗散系数变化规律基本一致,都随着剪切变形的增大,能量耗散系数逐渐增大,试件的能力耗散系数均大于0.8甚至超过0.9,塑性耗能能力强;试件RB4发生弯剪破坏,加载前期,试件的能量耗散系数整体呈上升趋势,具有较强的耗能能力,但后期由于翼缘端板焊缝撕裂破坏便退出工作。
2.5.3 应变分析
根据上述试验研究结果可知,剪切型耗能梁的抗震性能优于弯剪型耗能梁,且由于试件RB1~RB3的应变规律相似,现选取较为典型且能够反映各阶段应变发展趋势的试件RB3腹板和翼缘应变为例进行分析。
应变花沿试件腹板1/2高度两侧对称分布,布置于试件一侧,故选取一半测点进行分析。图14为试件RB3腹板的剪力-局部剪切应变曲线。由图14可知,试件未屈服前,剪力和应变呈现出明显的线性关系;试件屈服后应变增加明显,腹板出现局部屈曲变形,且随位移的增加,腹板屈曲程度加深,致使编号为(12,13,14)应变花局部剪切应变最大,其最大值为0.082。
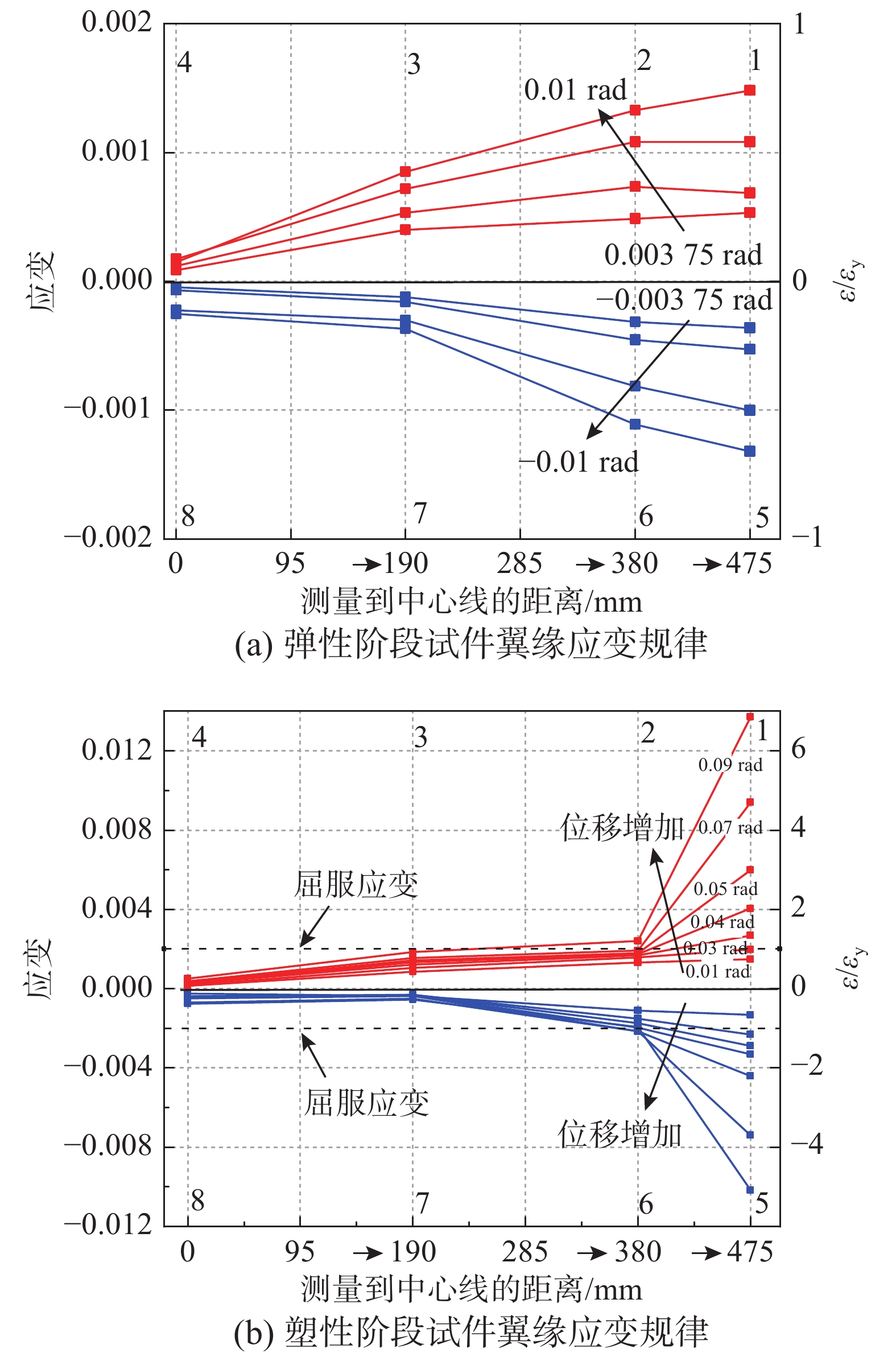
上下翼缘应变片沿试件长度方向布置。图15为试件RB3上下翼缘应变规律,由图15(a)可知,弹性阶段时,随着应变片到试件中心距离的增加,试件翼缘应变逐渐增大,且靠近试件梁端的应变最大,最大值约0.0015;加载位移继续增大,试件进入塑性阶段,如图15(b)所示,试件翼缘各位置的应变也随之出现不同程度的提高,但只有靠近翼缘端部的编号1、2、5、6应变片超过了屈服应变,这与试件梁端弯矩最大的受力特征相关且与试验中石灰脱落顺序特征相吻合。
3 试件可更换性能试验结果分析
耗能梁的可更换性能指的是地震过后,将受损的耗能梁拆卸下,然后安装新的耗能梁即可快速恢复结构的使用功能,其示意图见图16。本文耗能梁的可更换性能采用2个指标表征:1)耗能梁梁端残余转角γre, L,即耗能梁段可快捷拆卸时对应的梁端最大残余转角;2)与耗能梁相连的钢柱节点区的残余转角γre, C。
本次试验中耗能梁的更换过程仅采用常规扭矩扳手、铁锤头、钢钎等操作工具,由5名工人完成。各试件加载完成后首先将作动器水平荷载卸载为0,拆卸损伤耗能梁段,然后调整加载装置的水平位移至新的耗能梁可完全安装,确定此时对应的耗能梁梁端残余转角γre, L和双连肢钢柱节点区的残余转角γre, C。并在γre, L和γre, C下安装新的耗能梁段。可更换性评价指标如表5所示。需要注意的是,试验过程中测得双连肢钢柱节点区没有出现残余转角,节点区所出现的最大弹性转角通过该区域的对角线位移计测量数据计算所得。因此耗能梁的可更换性能由耗能梁梁端残余转角γre, L决定。
表 5 耗能梁的可更换性Table 5. Replaceability of energy dissipation beams试件编号 可更换时梁端
残余转角γre, L /rad连肢钢柱节点区的变形/rad 最大弹性转角 残余转角γre, C RB1 0.0046 0.000 32 − RB2 0.0034 0.000 38 − RB3 0.0033 0.000 22 − RB4 0.0020 0.000 30 − 各试件拆卸快捷,安装方便,拆卸时间约为安装时间的2/5,原因是在低周反复荷载作用下,耗能梁会产生损伤变形,致使耗能梁端连接构造的高强螺栓产生应力松弛,因此容易拆卸。各试件允许更换的最大梁端残余转角γre, L范围为0.0020 rad~0.0046 rad,试件RB1梁端残余转角γre, L最大为0.0046 rad,试件RB4梁端残余转角γre, L最小为0.0020 rad。其主要原因为,随着试件长度系数的增大,试件的破坏特征从腹板剪切屈服变形向梁端屈曲变形转变。剪切屈服型试件的残余变形主要集中在腹板撕裂区域,梁端区域残余变形较小,有利于梁端螺栓的拆卸,因此试件能够在更大的残余转角下进行更换。弯剪屈服型试件的残余变形主要集中于梁端区域,因此两侧连接区域的螺栓会因为变形过大而影响拆卸,所以试件RB4只能在梁段残余转角较小时才可进行更换。综上可知,试件RB1~RB3的可更换性能要优于试件RB4。
同时为保证新耗能梁能够在一定残余转角下顺利安装,需在连接处预设一定量的缝隙,新耗能梁试件在加工时建议比原构件长度尺寸进行缩短,较原试件缩短3 mm,待新耗能梁段安装后,缝隙用薄钢片等材料填充密实,不影响新“耗能”构件预定功能。
4 整体混合框架结构中试件的可更换性分析
通过对带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构进行基于性能的抗震设计,并对结构进行非线性静力分析及动力时程分析[19],结果表明,可更换耗能梁先于框架钢梁屈服且结构具有明显的可更换阶段。
为了解耗能构件在整体混合框架结构中的可更换能力,假设仅考虑耗能梁构件变形,而带可更换构件的RCS混合框架体系中其他构件均处于弹性或者保持刚性状态,取两层两跨的混合框架结构模型。根据其几何关系[42],耗能构件的变形与整体混合结构变形满足式(5),即:
e\gamma = \theta L (5) 式中:γ为耗能梁的剪切变形;θ为整体混合框架层间位移角;L为耗能框架的跨度。混合框架结构模型几何变形如图17所示。
研究表明[19],带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构在正常使用阶段、耗能构件可更换阶段和生命安全阶段的层间位移角限值分别为1/400、1/160和1/60。根据式(5)可以计算得到本文4个耗能梁的剪切变形,如表6所示。
结合可更换耗能梁的试验现象及可更换性,对整体混合框架结构中耗能构件的可更换性进行分析。由表6可知,RCS混合框架处于正常使用阶段时,计算所得试件RB1~RB3的剪切变形均大于表4所得耗能梁的屈服转角γy,试件RB4的剪切变形小于表4所得耗能梁的屈服转角γy,说明试件RB1~RB3能够在混合框架处于弹性阶段时进入屈服,而试件RB4在此阶段始终处于弹性阶段;在耗能构件可更换阶段,计算所得试件RB4的剪切变形大于表4所得耗能梁的屈服转角0.00467 rad,说明试件RB4进入屈服,说明在此阶段所有试件处于弹塑性阶段;整体结构处于生命安全阶段时,计算所得试件RB1~RB3的剪切变形小于0.04 rad,结合耗能梁加载过程可知,试件RB1~RB3处于部分损伤阶段,而试件RB4此时发生翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂现象。
表 6 耗能梁的变形能力Table 6. Deformability of energy dissipation beamsRCS混合框架结构
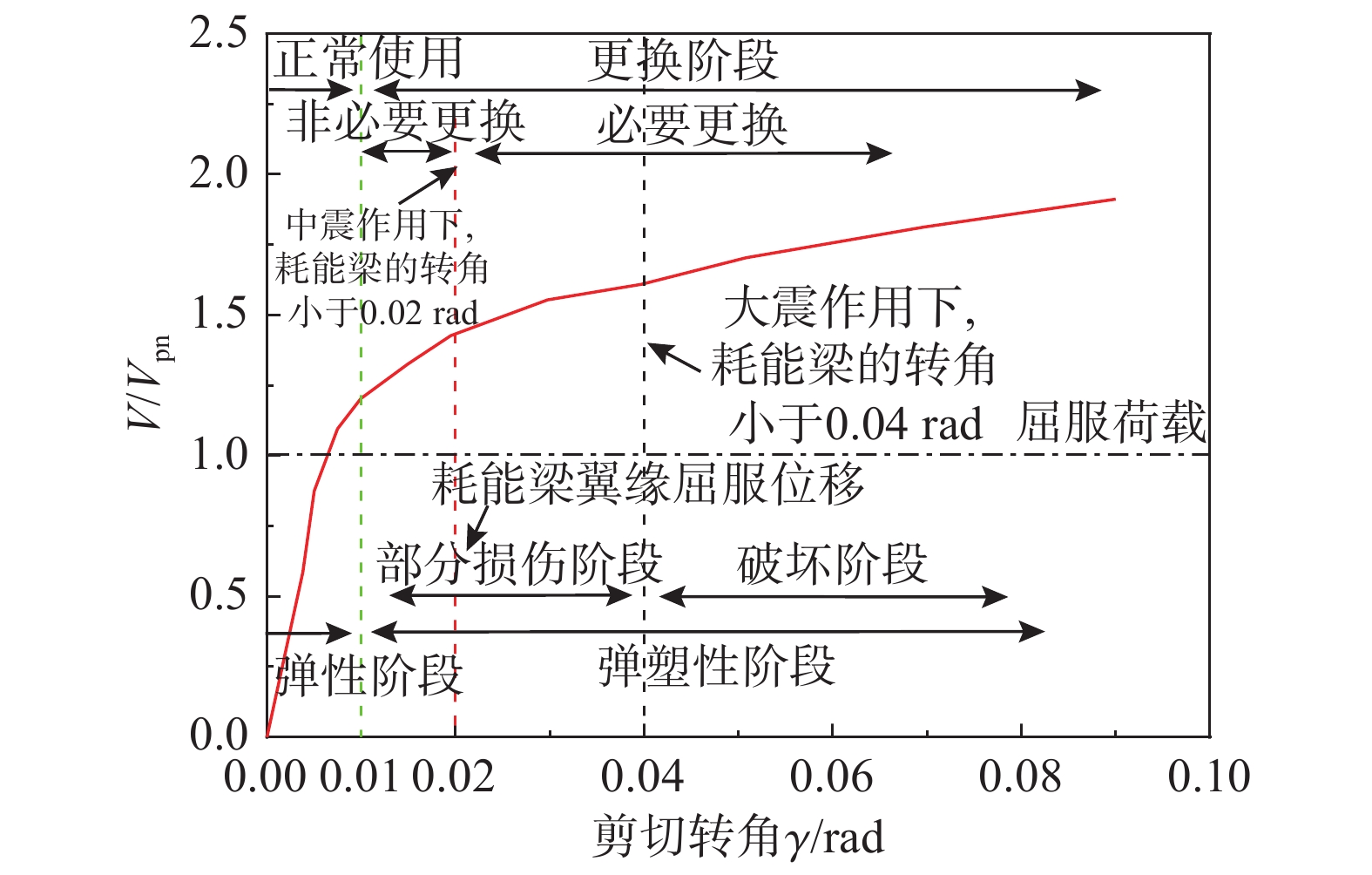
层间位移角限值耗能梁的剪切变形/rad RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 正常使用 1/400 0.0047 0.0043 0.0039 0.0034 耗能构件可更换 1/160 0.0118 0.0106 0.0099 0.0086 生命安全 1/60 0.0315 0.0284 0.0263 0.0230 根据试验加载过程中试件的损伤特征以及上述分析,试件的可更换性与整体混合结构的关系如图18所示。图18中,竖向坐标为试件抗剪承载力与屈服剪力的比值,横向坐标为试件剪切转角。在整个加载过程中,根据耗能梁的损伤特征,弹塑性阶段包括部分损伤阶段和破坏阶段,耗能梁的可更换性能包括正常使用阶段和可更换阶段,其中可更换阶段按照翼缘是否屈服又可分为非必要更换阶段和必要更换阶段。非必要更换阶段为耗能梁腹板屈服而翼缘未屈服,考虑耗能梁的强度储备以及试件未出现明显损伤,且后期还具有较大的“耗能”能力,在一定程度上,可以继续使用;必要更换阶段为耗能梁出现翼缘屈服、腹板屈曲和撕裂等损伤,必须更换。
5 结论
本文通过对4个不同长度系数的可更换耗能梁进行低周往复加载试验,以研究可更换耗能梁的抗震及可更换性能,得到的主要结论如下:
(1)长度系数为0.68~1.05的试件,即试件RB1~RB3发生了剪切破坏,破坏特征主要为腹板-加劲肋焊缝撕裂、腹板屈曲和腹板撕裂;长度系数为1.60的试件,即试件RB4发生了弯剪破坏,破坏特征主要包括梁端翼缘-端板焊缝撕裂和梁端翼缘屈曲。
(2)各试件的滞回曲线非常饱满,具有优异的变形能力和耗能能力;随着塑性转角的增大,试件的受剪承载力强化明显,直到破坏前没有出现承载力下降。
(3)给出剪切型破坏的试件超强系数建议取值为1.90;发生剪切型破坏的试件最小极限塑性转角为0.0871大于AISC 341-10规定耗能梁塑性转角0.08 rad的限值要求;剪切型破坏试件的平均累积塑性转角为1.32 rad,弯剪型破坏试件累积塑性转角为0.97 rad,剪切型试件比弯剪型试件提高了约36%;试件的能量耗散系数均大于0.8,具有良好的变形能力和耗能能力。
(4)根据耗能梁构件与带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构体系几何变形关系,小震作用下,构件处于正常使用阶段;中震作用下,构件处于非要可更换阶段;大震作用下,构件处于必要更换阶段。
-
表 1 材料性能
Table 1 Material properties
钢材类型 部位 厚度t/mm 屈服强度fy/MPa 抗拉强度fu/MPa 强屈比fu/fy 屈服应变εy/με 弹性模量E/(×105MPa) 延伸率δ/(%) Q235 耗能梁腹板 10 291.7 441.7 1.51 1383 2.11 41.5 Q345 耗能梁翼缘和钢柱腹板 18 391.7 538.3 1.37 1967 1.99 42.5 Q345 钢柱翼缘 25 443.2 554.5 1.25 2161 2.07 42.7 表 2 试件参数
Table 2 Specimen parameters
试件
编号截面形式/
(mm×mm×mm×mm)耗能梁
长度e/mm长度系数
e/(Mp/Vp)加劲肋布置 试件
梁端构造间距d/mm 布置
形式RB1 I400×200×10×18 740 0.68 4@185 双侧 端板螺栓
连接RB2 940 0.86 5@188 RB3 1140 1.05 6@190 RB4 1740 1.60 8@218 表 3 试件抗剪承载力和超强系数
Table 3 Shear capacity and overstrength of specimens
试件
编号实测屈曲
剪力Vpn/kN极限抗剪
承载力Vu/kN超强
系数ΩRB1 573.3 1190.1 2.07 RB2 573.3 1133.4 1.98 RB3 573.3 1131.0 1.97 RB4 573.3 894.5 1.56 表 4 试件变形能力
Table 4 Deformation capacity of specimens
试件
编号屈服转角
γy/rad极限塑性
转角γp/rad累积塑性转角
Σγp/rad累积延性
系数Σγp/γyRB1 0.00225 0.0877 1.26 560 RB2 0.00292 0.0871 1.38 473 RB3 0.00234 0.0876 1.32 564 RB4 0.00467 0.0652 0.97 208 表 5 耗能梁的可更换性
Table 5 Replaceability of energy dissipation beams
试件编号 可更换时梁端
残余转角γre, L /rad连肢钢柱节点区的变形/rad 最大弹性转角 残余转角γre, C RB1 0.0046 0.000 32 − RB2 0.0034 0.000 38 − RB3 0.0033 0.000 22 − RB4 0.0020 0.000 30 − 表 6 耗能梁的变形能力
Table 6 Deformability of energy dissipation beams
RCS混合框架结构
层间位移角限值耗能梁的剪切变形/rad RB1 RB2 RB3 RB4 正常使用 1/400 0.0047 0.0043 0.0039 0.0034 耗能构件可更换 1/160 0.0118 0.0106 0.0099 0.0086 生命安全 1/60 0.0315 0.0284 0.0263 0.0230 -
[1] GB 50011−2010, 建筑抗震设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010. GB 50011−2010, Code for seismic design of buildings [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
[2] 吕西林, 武大洋, 周颖. 可恢复功能防震结构研究进展[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2019, 40(2): 1 − 15. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2019.02.001 LYU Xilin, WU Dayang, ZHOU Ying. State-of-the-art of earthquake resilient structures [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2019, 40(2): 1 − 15. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2019.02.001
[3] EATHERTON M R, MA X, KRAWINKLER H, et al. Quasi-static cyclic behavior of controlled rocking steel frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2014, 140(11): 04014083. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001005
[4] CLAYTON P M, BERMAN J W, LOWES L N. Subassembly testing and modeling of self-centering steel plate shear walls [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 56: 1848 − 1857. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.06.030
[5] 姜子钦, 杨晓峰, 张爱林, 等. 带可更换抗侧耗能装置的装配式钢框架结构静力性能研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(4): 365 − 373, 382. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020110040 JIANG Ziqin, YANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Ailin, et al. Study on static behavior of steel frame structure with lateral resistance energy-consuming device [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(4): 365 − 373, 382. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020110040
[6] 张浩, 连鸣, 苏明周, 等. 带可更换低屈服点耗能梁段-端板连接的钢框筒结构抗震性能试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(7): 28 − 42. ZHANG Hao, LIAN Ming, SU Mingzhou, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of steel framed-tube structure with end-plate connected replaceable shear links made of low yield point steel [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(7): 28 − 42. (in Chinese)
[7] ZHANG H, SU M Z, LIAN M, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the seismic behavior of high-strength steel framed-tube structures with end-plate-connected replaceable shear links [J]. Engineering Structures, 2020, 223: 111172. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.111172
[8] LIAN M, GUAN B L, CHENG Q Q, et al. Experimental and numerical study of seismic performance of high-strength steel fabricated framed-tube structures with replaceable shear links [J]. Structures, 2020, 28: 2714 − 2732. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2020.10.081
[9] 纪晓东, 王彦栋, 马琦峰, 等. 可更换钢连梁抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(10): 1 − 10. JI Xiaodong, WANG Yandong, MA Qifeng, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of replaceable steel coupling beams [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2015, 36(10): 1 − 10. (in Chinese)
[10] JI X D, WANG T D, MA Q F, et al. Cyclic behavior of replaceable steel coupling beams [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2017, 143(2): 04016169. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001661
[11] MANSOUR N, CHRISTOPOULOS C, TREMBLAY R. Experimental validation of replaceable shear links for eccentrically braced steel frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2011, 137(10): 1141 − 1152. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000350
[12] SHEN Y L, CHRISTOPOULOS C, MANSOUR N, et al. Seismic design and performance of steel moment-resisting frames with nonlinear replaceable links [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2011, 137(10): 1107 − 1117. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000359
[13] JI X D, LIU D, SUN Y, et al. Seismic performance assessment of a hybrid coupled wall system with replaceable steel coupling beams versus traditional RC coupling beams [J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2017, 46(4): 517 − 535.
[14] YAO Z C, WANG W, FANG C, et al. An experimental study on eccentrically braced beam-through steel frames with replaceable shear links [J]. Engineering Structures, 2020, 206: 110185. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.110185
[15] 谢鲁齐, 吴京, 章锦洋, 等. 可更换耗能连接力学机理及变形性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(6): 186 − 195. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.08.0475 XIE Luqi, WU Jing, ZHANG Jinyang, et al. Study on the mechanical and deformation properties of replaceable energy dissipation connectors [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(6): 186 − 195. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.08.0475
[16] 孙东德, 杨勇, 马银科, 等. 采用单侧角钢的梁柱可更换连接件抗震性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2022, 39(4): 151 − 163. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.02.0122 SUN Dongde, YANG Yong, MA Yinke, et al. Experimental study on seismic performance of replaceable beam-column connector with single-sided angle steel [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2022, 39(4): 151 − 163. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.02.0122
[17] 黄炜, 胡高兴. 可恢复预制装配式RC梁柱节点抗震性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2022, 39(12): 165 − 176, 189. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.07.0554 HUANG Wei, HU Gaoxing. Seismic performance of earthquake-resilient precast rc beam-column joints [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2022, 39(12): 165 − 176, 189. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.07.0554
[18] 叶建峰, 郑莲琼, 颜桂云, 等. 装配式可更换耗能铰滞回性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(8): 42 − 54. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0531 YE Jianfeng, ZHENG Lianqiong, YAN Guiyun, et al. Experimental study on hysteretic performance of replaceable energy-dissipating prefabricated hinges [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(8): 42 − 54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.07.0531
[19] 门进杰, 霍文武, 兰涛, 等. 基于刚度和位移带可更换构件RCS混合框架结构抗震设计方法[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(4): 169 − 178. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.06.0370 MEN Jinjie, HUO Wenwu, LAN Tao, et al. Seismic design method of RCS hybrid frame structure with replaceable members based on stiffness and displacement [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(4): 169 − 178. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.06.0370
[20] 门进杰, 霍文武, 兰涛, 等. 带可更换构件的RCS混合框架结构受力特性及抗震设计方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(6): 42 − 52. MEN Jinjie, HUO Wenwu, LAN Tao, et al. Mechanical behavior and seismic design method of RCS hybrid frame structure with replaceable components [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(6): 42 − 52. (in Chinese)
[21] ANSI/AISC 341-10, Seismic provisions for structural steel buildings [S]. Chicago: American Institute of Steel Construction, 2010.
[22] ROSSI P P, LOMBARDO A. Influence of the link overstrength factor on the seismic behaviour of eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2007, 63(11): 1529 − 1545. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2007.01.006
[23] AZAD K S, TOPKAYA C. A review of research on steel eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 128: 53 − 73. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.07.032
[24] MCDANIEL C C, UANG C M, SEIBLE F. Cyclic testing of built-up steel shear links for the new bay bridge [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 801 − 809. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2003)129:6(801)
[25] RICHARDS P, UANG C M. Development of testing protocol for short links in eccentrically braced frames [R]. San Diego: University of California at San Diego, 2003.
[26] OKAZAKI T, ENGELHARDT M D. Cyclic loading behavior of EBF links constructed of ASTM A992 steel [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2007, 63(6): 751 − 765. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2006.08.004
[27] 王彦栋. 带RC楼板的可更换钢连梁抗震性能及设计方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016. WANG Yandong. Study on seismic behavior and design of replaceable steel coupling beams with RC slabs [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[28] GÁLVEZ P. Investigation of factors affecting web fractures in shear links [D]. Austin: The University of Texas at Austin, 2004.
[29] 纪晓东, 马琦峰, 王彦栋, 等. 钢连梁可更换消能梁段抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2014, 35(6): 1 − 11. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2014.06.002 JI Xiaodong, MA Qifeng, WANG Yandong, et al. Cyclic tests of replaceable shear links in steel coupling beams [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2014, 35(6): 1 − 11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2014.06.002
[30] HJELMSTAD K D, POPOV E P. Seismic behavior of active beam links in eccentrically braced frames [R]. Berkeley: University of California, 1983.
[31] ENGELHARDT M D, POPOV E P. Behavior of long links in eccentrically braced frames [R]. Berkeley: University of California, 1989.
[32] RYU H C. Effects of loading history on the behavior of links in seismic resistant eccentrically braced frames [D]. Austin: University of Texas at Austin, 2005.
[33] ARCE G, OKAZAKI T, ENGELHARDT M D. Experiments on the impact of higher strength steels on local buckling and overstrength of links in EBFs [R]. Austin: University of Texas at Austin, 2001.
[34] OKAZAKI T, ENGELHARDT M D, HONG J K, et al. Improved link-to-column connections for steel eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2015, 141(8): 04014201. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001041
[35] OKAZAKI T, ENGELHARDT M D, NAKASHIMA M, et al. Experimental performance of link-to-column connections in eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2006, 132(8): 1201 − 1211. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2006)132:8(1201)
[36] STEPHENS M, DUSICKA P. Continuously stiffened composite web shear links: Tests and numerical model validation [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2014, 140(7): 04014040. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000996
[37] DUSICKA P, ITANI A M, BUCKLE I G. Cyclic behavior of shear links of various grades of plate steel [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2010, 136(4): 370 − 378. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000131
[38] LIU X G, FAN J S, LIU Y F, et al. Experimental research of replaceable Q345GJ steel shear links considering cyclic buckling and plastic overstrength [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 134: 160 − 179. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.03.018
[39] KASAI K, POPOV E P. A study of seismically resistant eccentrically braced steel frame systems [R]. Berkeley: University of California, 1986.
[40] MALLEY J O, POPOV E P. Shear links in eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1984, 110(9): 2275 − 2295. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:9(2275)
[41] RICLES J M, POPOV E P. Experiments on eccentrically braced frames with composite floors [R]. Berkeley: University of California, 1987.
[42] HJELMSTAD K D, POPOV P E. Characteristics of eccentrically braced frames [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1984, 110(2): 340 − 353. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:2(340)
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: